On Saturday, October 22, the Watershed Protection Program joined scientists from the Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University’s Fisheries Team (ANS) to survey for fish in Ridley Creek at Ashbridge Preserve. It was a beautiful Saturday morning — crisp, bright, and perfect for learning more about the wildlife that calls Ridley Creek home! This event provided a unique opportunity to get a fish’s eye view of stream health, and it would not have been possible without the wonderful support of the talented Fisheries Team members Dr. David Keller and Paul Overbeck.
The morning started with a primer on fish survey protocols. Paul walked volunteers through the mechanics of electrofishing, a sampling technique where a small electric current is passed through the water to stun fish just long enough to be scooped up in a net and placed in a bucket. The scientists headed into Ridley Creek and began to survey, and immediately there was action in the water!
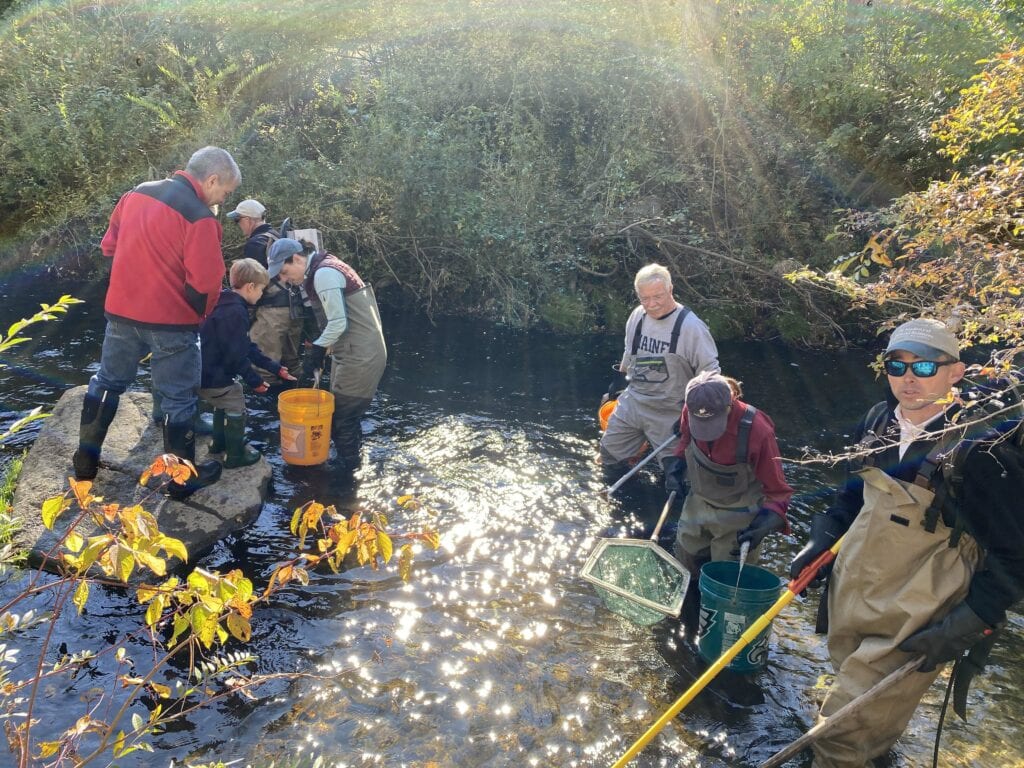

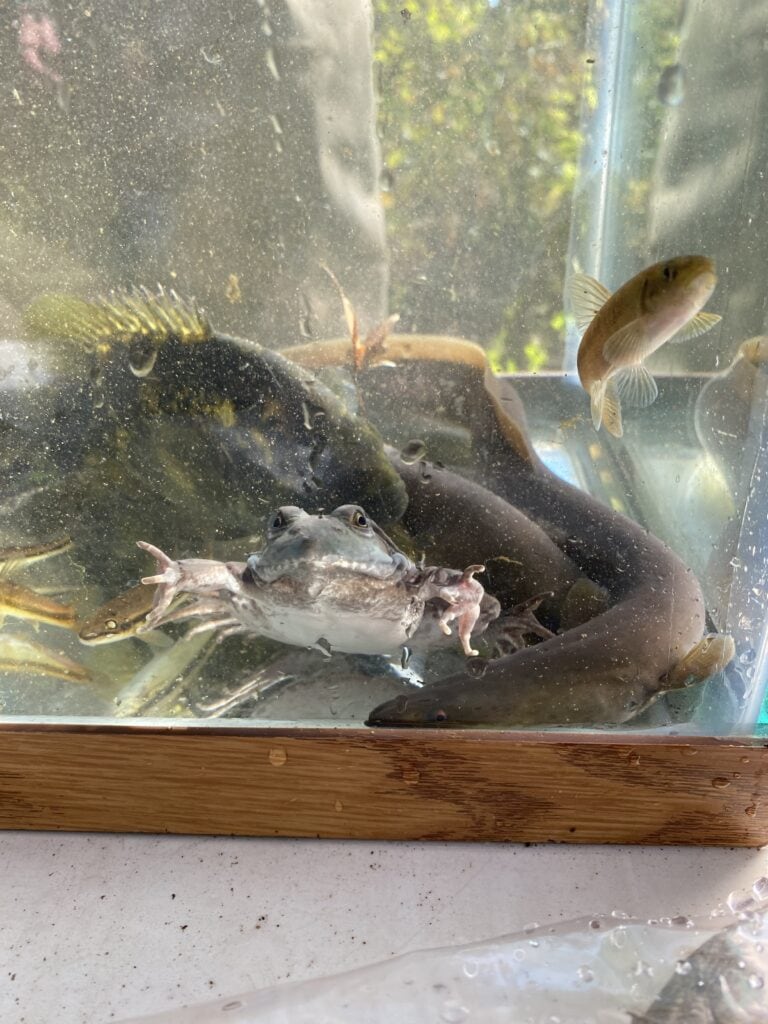
As stunned fish began to fill the buckets, they were brought to shore and placed in aquariums to be studied. Within a short period of time, over 10 species of fish, crustaceans, and amphibians were documented. The Fisheries scientists quickly began to identify the wildlife and share what the presence of these creatures means for the ecosystem of Ridley Creek and surrounding landscape. Once the fish were observed in the aquariums, they were all safely released back into Ridley Creek.
Included in the fishes that were identified was the American eel (Anguilla rostrata), a fish that migrates thousands of miles in its lifetime. This fish breeds in the Sargasso sea and migrates to headwater ecosystems — like at Ashbridge Preserve — where they can live over 25 years before completing their migration. The presence of this incredible fish showcases the connectivity of Ridley Creek with no large barriers to stop their movement to and from the Atlantic Ocean. American eel populations are declining due to large dams that block their migration, contribute to habitat loss, and overfishing of young eels.

Another fascinating fish present in the stream is the cutlip minnow (Exoglossum maxillingua). These fish are easy to identify up close, with a specially adapted three lobed, lower lip. These fish prefer gravel and rocky bottomed streams and are unable to thrive in polluted waterways where fine sediment buries rocky habitat.
Black nose dace (Rhinichthys atratulus) are one of the most visibly common fishes in the headwaters of Ridley Creek and were abundant in the sample collected by ANS scientists! These fish are small, with big fish growing to be less than 4 inches long, but they school in shallow clear waters and can often be seen from the stepping stones at Ashbridge Preserve.
Fallfish (Semotilus corporalis) is the largest minnow native to eastern North America and they are abundant in the Ridley Creek headwaters! They are excellent targets for anglers, and their energetic behavior has earned them the nickname “freshwater tarpon.”
Rock Bass (Ambloplites rupestris) is well known to anglers as a sport fish, but this fish is actually an introduced species in Pennsylvania waterways! Since being introduced some time in the 1880s, they are actively stocked in waterways throughout the state.
In addition to the fish that were sampled from Ridley Creek, ANS brought preserved specimens of fish of interest, including the northern snakehead (Channa argus), an aggressive invasive fish that has been spreading throughout the Delaware River watershed.
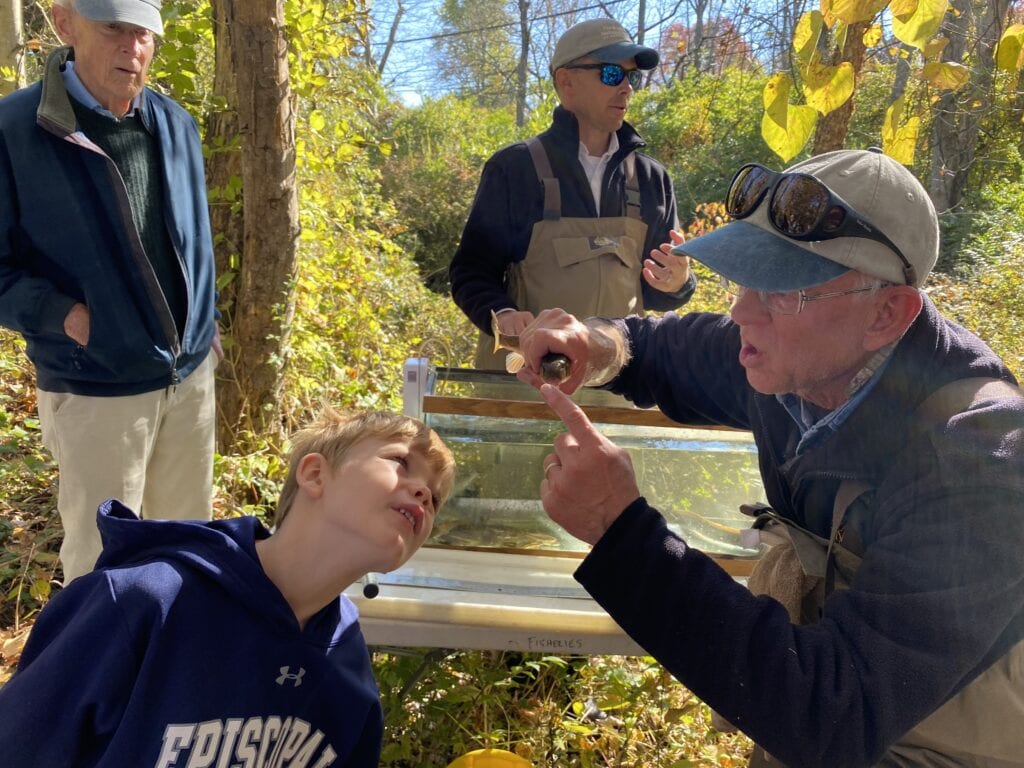

This exciting and fascinating experience highlighted the importance of the ways that our activities on the landscape impacts the many lifeforms that call Ridley Creek home. The presence or absence of different species of fish can inform researchers of the health of Ridley Creek. There is a clear relationship with the development of the landscape and the decreasing health of freshwater ecosystems resulting in the loss of indicator species. As species disappear from the ecosystem, the entire system becomes weaker. As we head into a future that includes more frequent large storms, it is important that we focus on understanding how we can strengthen and improve the health of our systems to create resilience — the first step in this process is looking at who is present in the ecosystem.
A huge thanks to the Fisheries Team for sharing their immense knowledge and skill! Click here to learn more about ongoing Fisheries research!
For more information on the research being conducted by the Watershed Protection Program and the lessons we have been learning about water quality in Ridley, Crum, and Darby Creeks, please explore the State of Our Streams Report.
— By Watershed Protection Program Director Lauren McGrath