Rushton Farm Bird Banding Station | Annual Year in Review 2021

The vertiginous year of 2021 began with early spring vaccinations spurring the human world to return to its usual frenetic pace in the “aftermath” of the COVID-19 pandemic. Businesses, gatherings, travel, and development resumed with vigor—and the relative quiescent lull the earth had experienced in 2020 was no more. Did the natural world benefit in some small way by briefly quieting its human inhabitants? Maybe we’ll never be able to quantify it, but when the bird banders got back together at Rushton Woods Preserve last spring, it was clear (and comforting) that the birds kept on living their celestial lives: lives that were intricately synchronized with the steady rhythms of nature millions of years before we showed up.
A small songbird weighing just a little more than a quarter may spend 30% of its year in migration, traveling to and from the exact breeding and wintering locations as the year before. Scientists are still trying to understand all the mysterious physiological mechanisms that allow these tiny athletes to make such intense journeys. Each spring an estimated three billion North American migratory birds traverse distances of over 2,000 miles from the tropical wintering grounds of South America to the critical boreal forest “nursery” of Canada—most of them putting in the mileage by night, navigating by starlight and Earth’s magnetic field. This anomalous strategy allows foraging by day along the way, which is vital especially for smaller birds that can only carry so much fuel in the form of fat reserves.

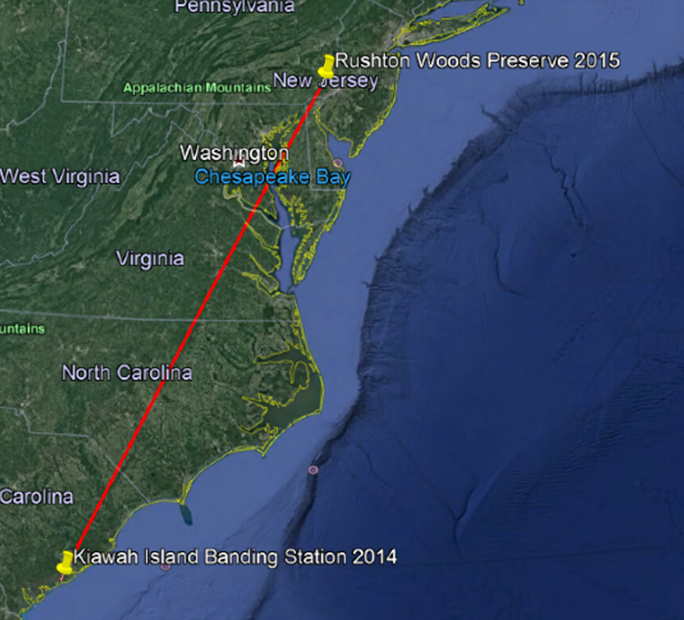
In fact for most birds, 70% of migration is spent feeding and resting in “stopover habitat”, or pit stops, rather than in sustained directional flight. Consequently, understanding how birds use stopover habitat during migration has become just as important to ornithologists as identifying breeding or wintering habitat. This is just one of the reasons why we began banding at Rushton Woods Preserve and Farm twelve years ago. Never was the stopover value of our nature preserve better elucidated than on the morning of May 4th, 2021.
The Spring Fallout
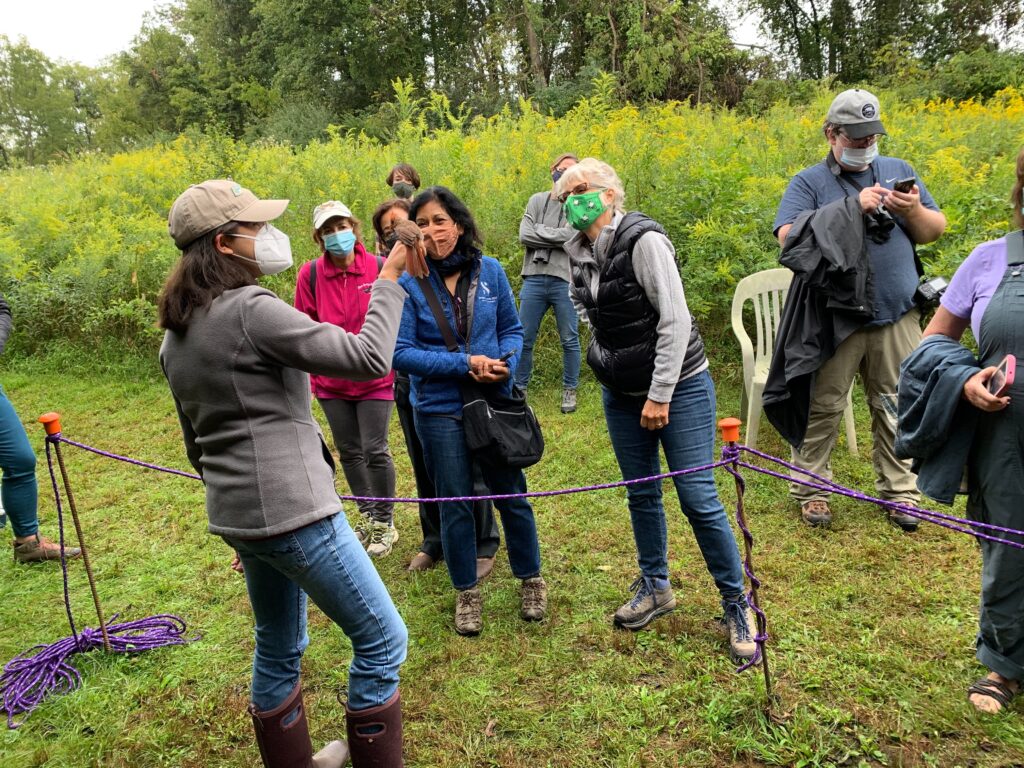
Bleary-eyed banders arrived to the hedgerows in the blue civil twilight before dawn, expecting a good catch based on the southerly winds the previous night. As the nets were opened, the vegetation around us came alive with the whispered din of hundreds of excited bird voices chirping of their recent arrival. The low chattering exploded into full song at daybreak, and it was as if we had just entered an aviary with the roar of hundreds of birds of dozens of different species reverberating through the shrubs and vines. “It’s birdy as heck out here today,” I noted, now wide-eyed, as we convened at the banding table to anticipate the first net check.
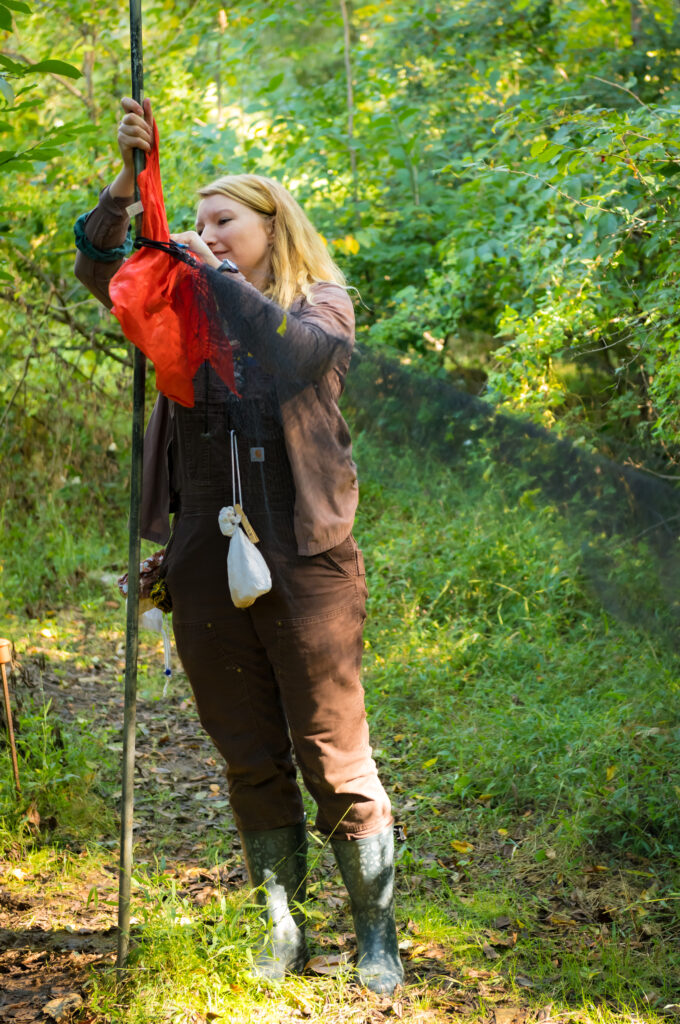

Favorable migration conditions the previous night combined with pre-dawn storms presented fallout conditions (whereby birds cannot continue to their destination because of the energy required to fly through severe weather) with many travelers honing in on the closest suitable stopover sanctuary. The “good catch” we expected became our best catch ever with 180 individuals being safely processed and released by our skilled team of 4 licensed banders and 7 volunteers, plus a few friends from the PA Game Commission who happened to be visiting that day.
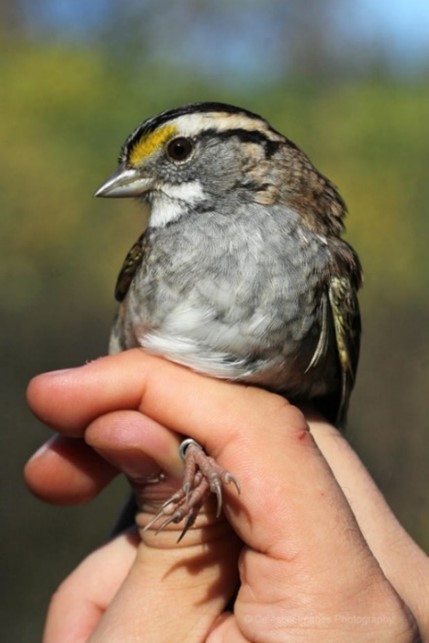
The avian cast included our first Brewster’s Warbler (defined as a hybrid of the Blue-winged Warbler and the near threatened Golden-winged Warbler) along with a dazzling 24 other species: Magnolia Warbler, American Redstart, Ovenbird, Blue-winged Warbler, Common Yellowthroat, Northern Waterthrush, Black-throated Blue Warbler, Black-and-white Warbler, Yellow-rumped Warbler, Wood Thrush, Veery, White-eyed Vireo, Eastern Towhee, Gray Catbird, American Goldfinch, Swamp Sparrow, White-throated Sparrow, and White-crowned Sparrow!
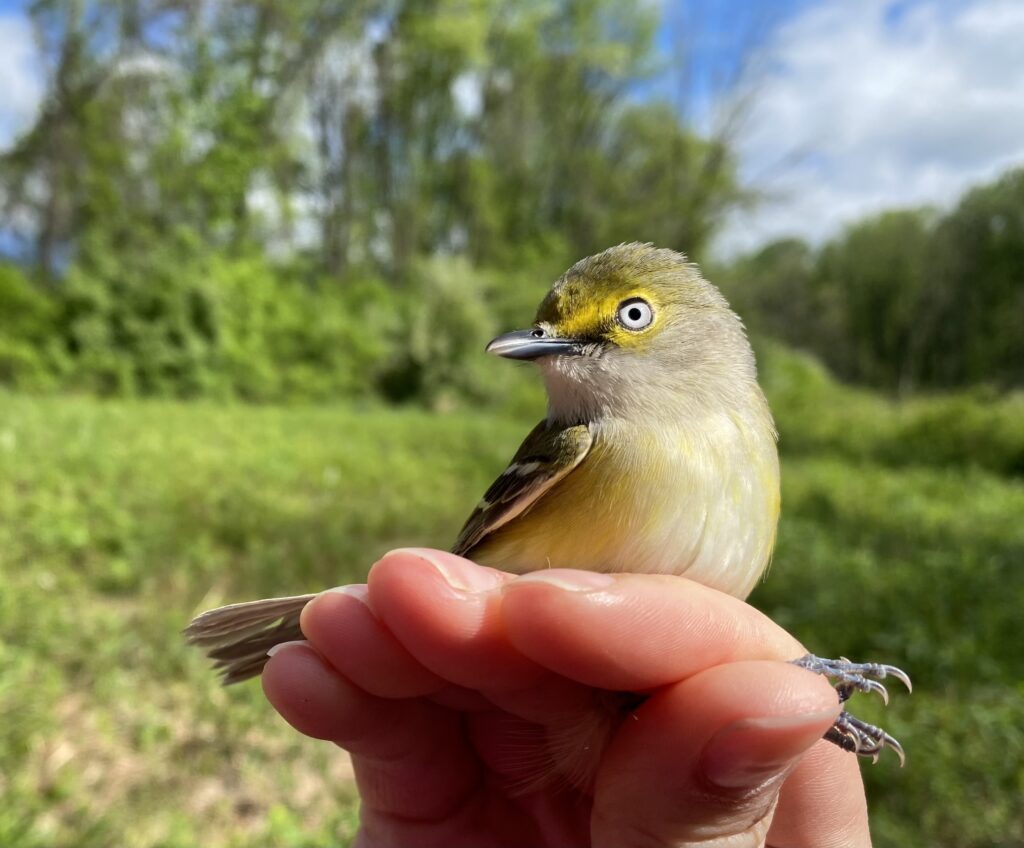
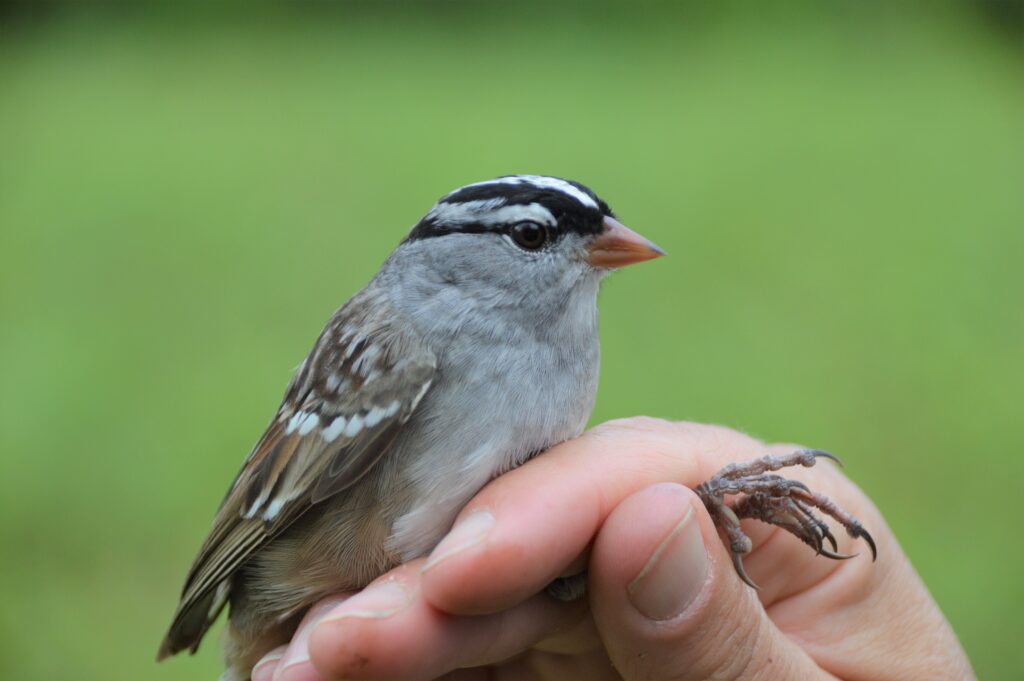
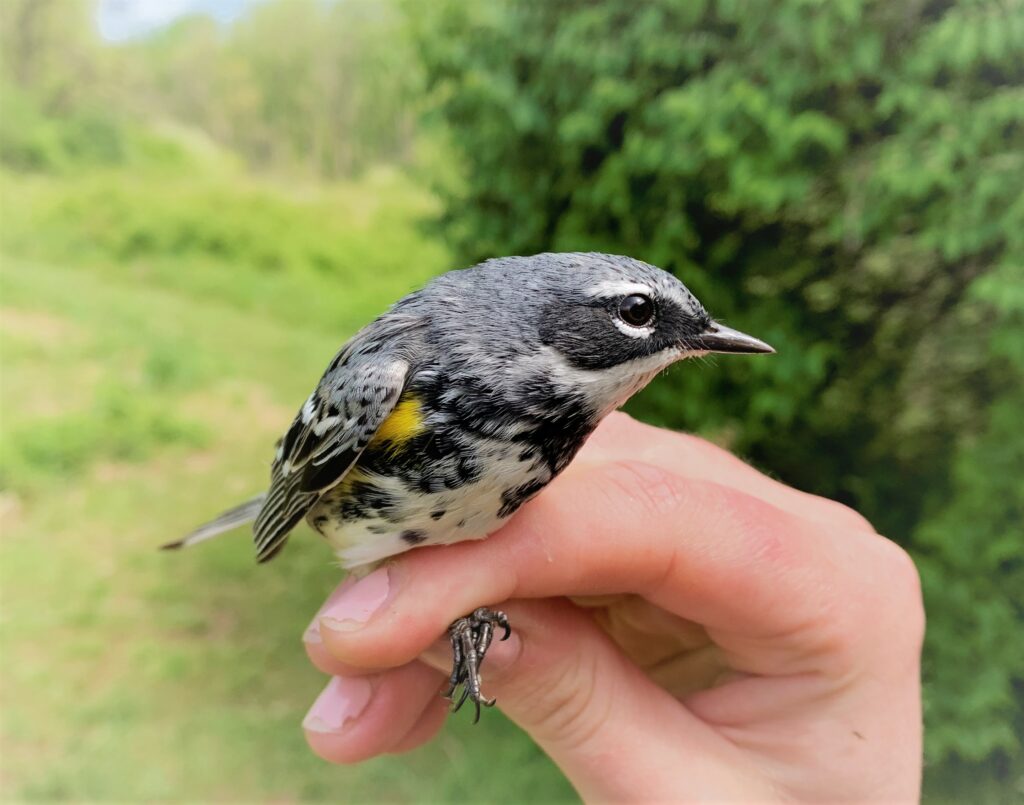
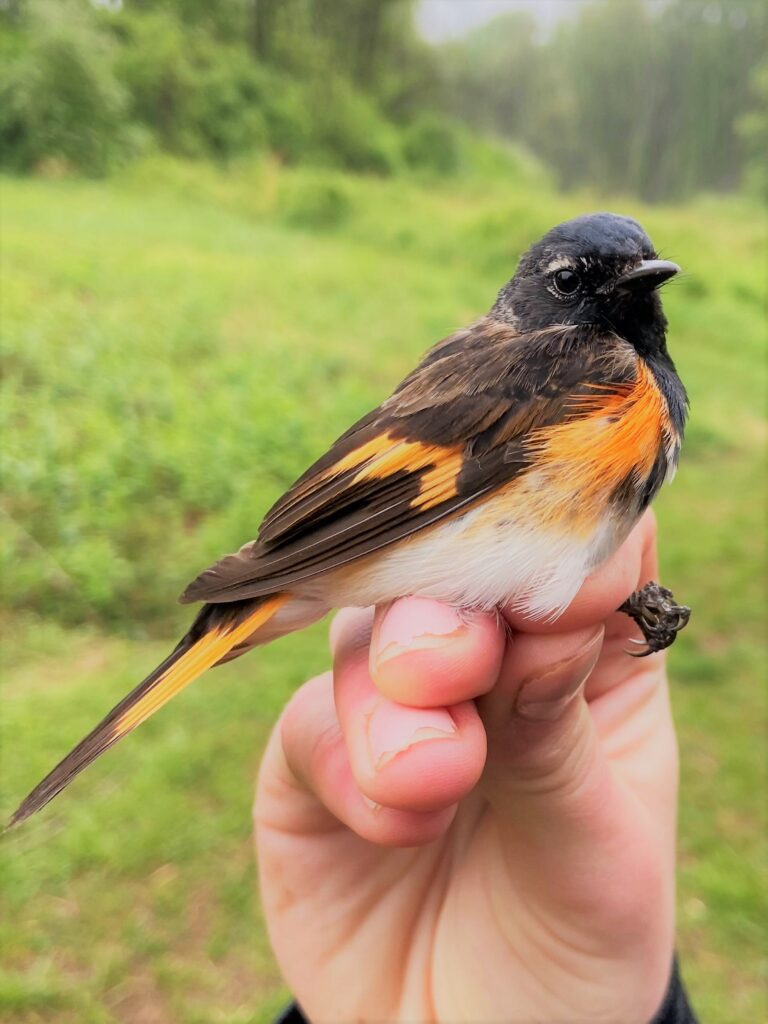
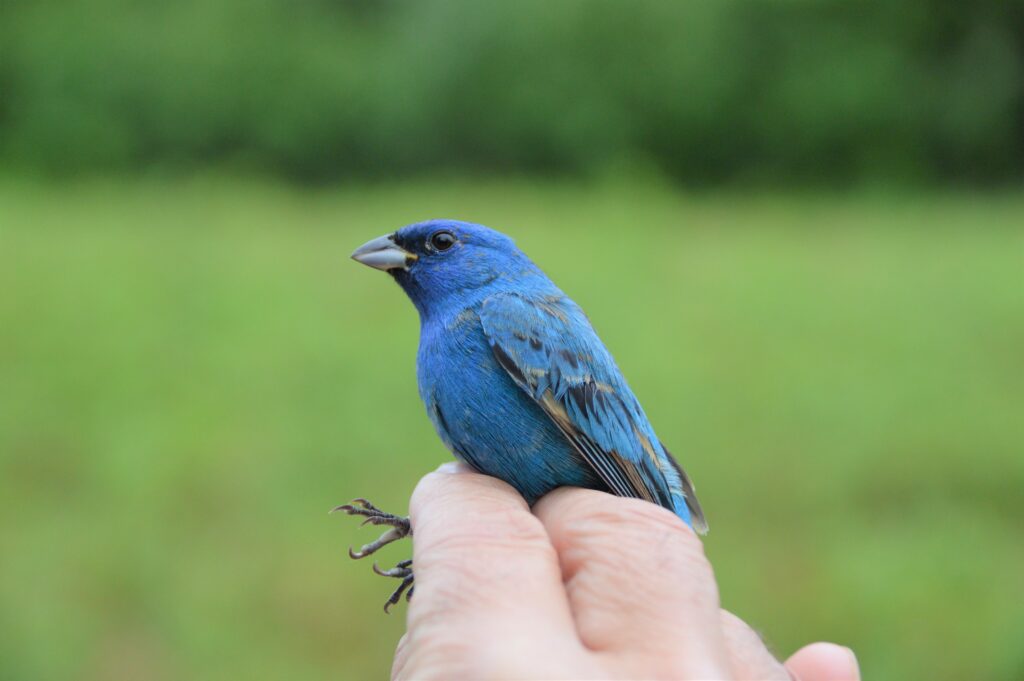
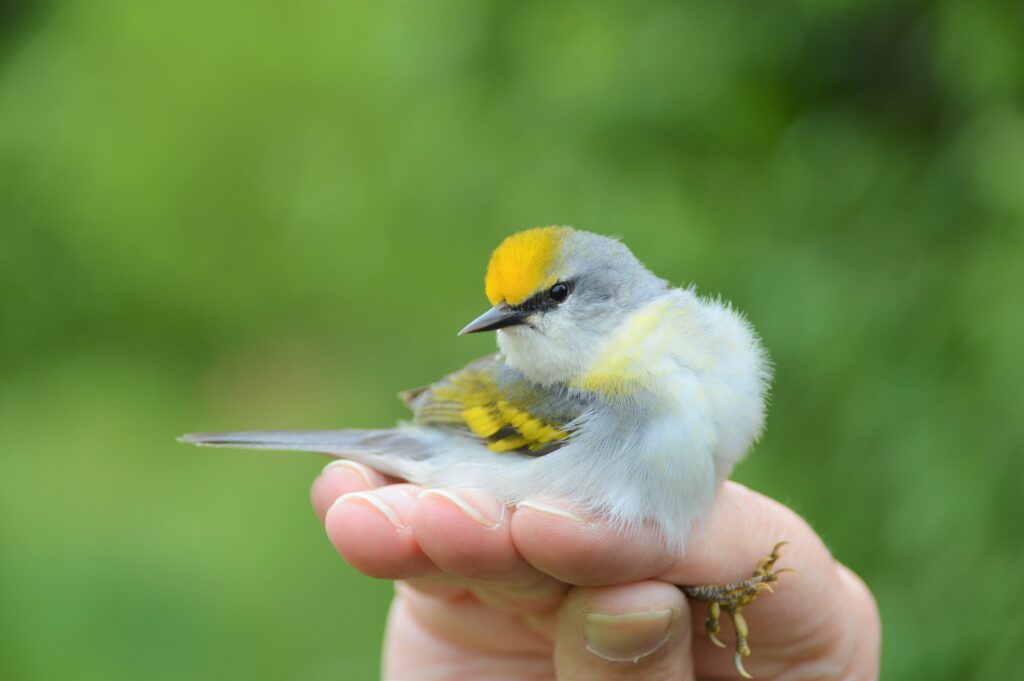
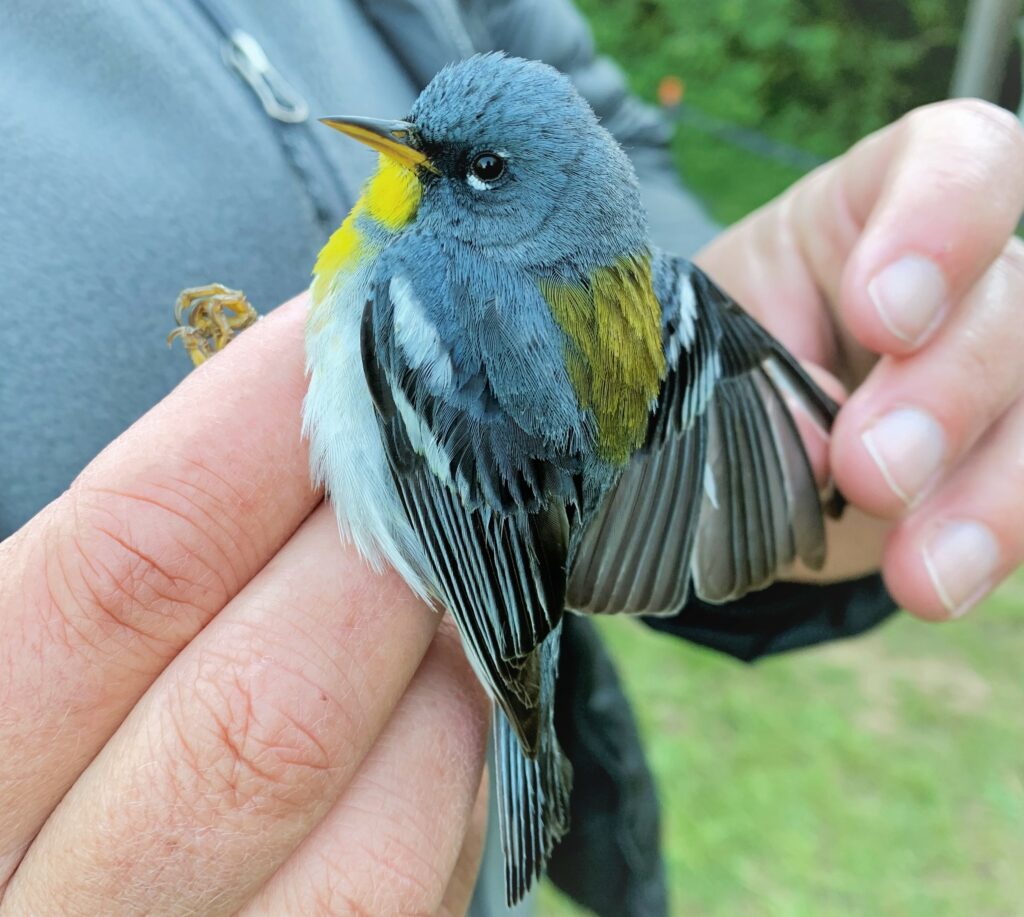
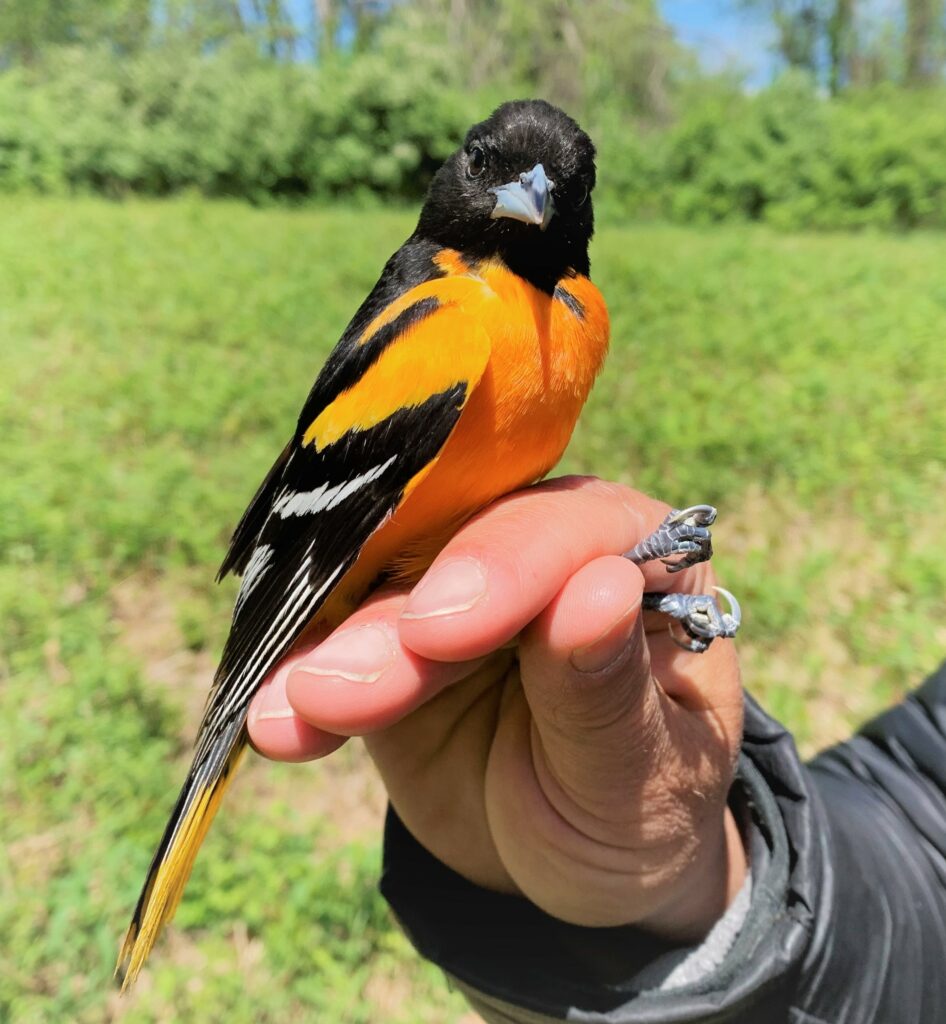









A Summer Breeding Record
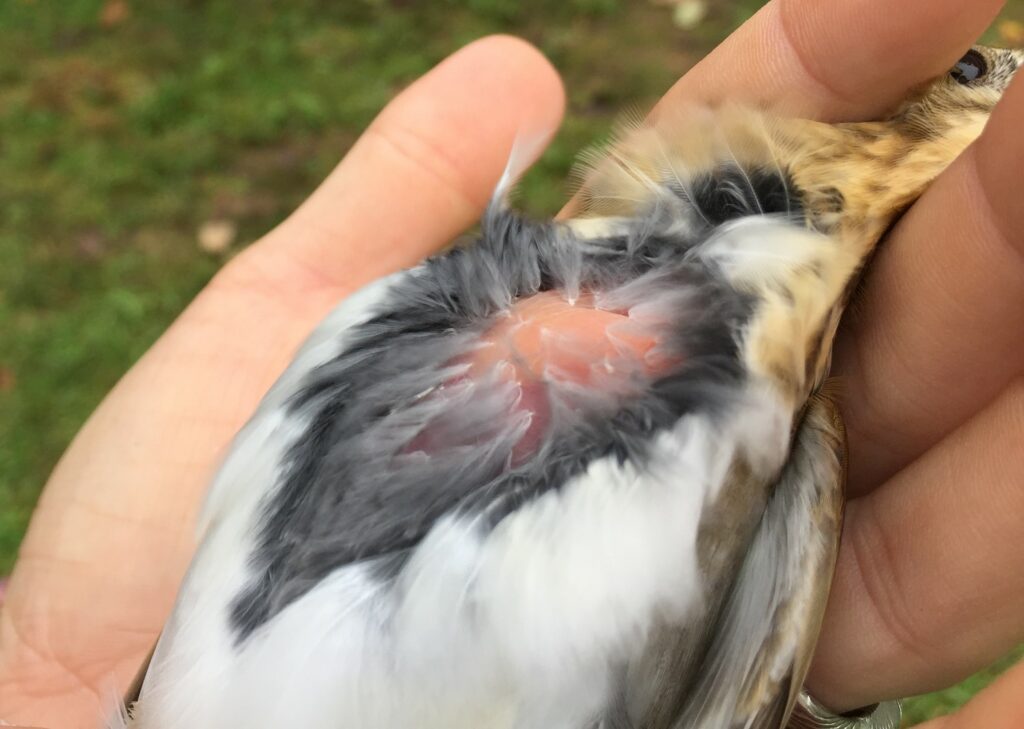
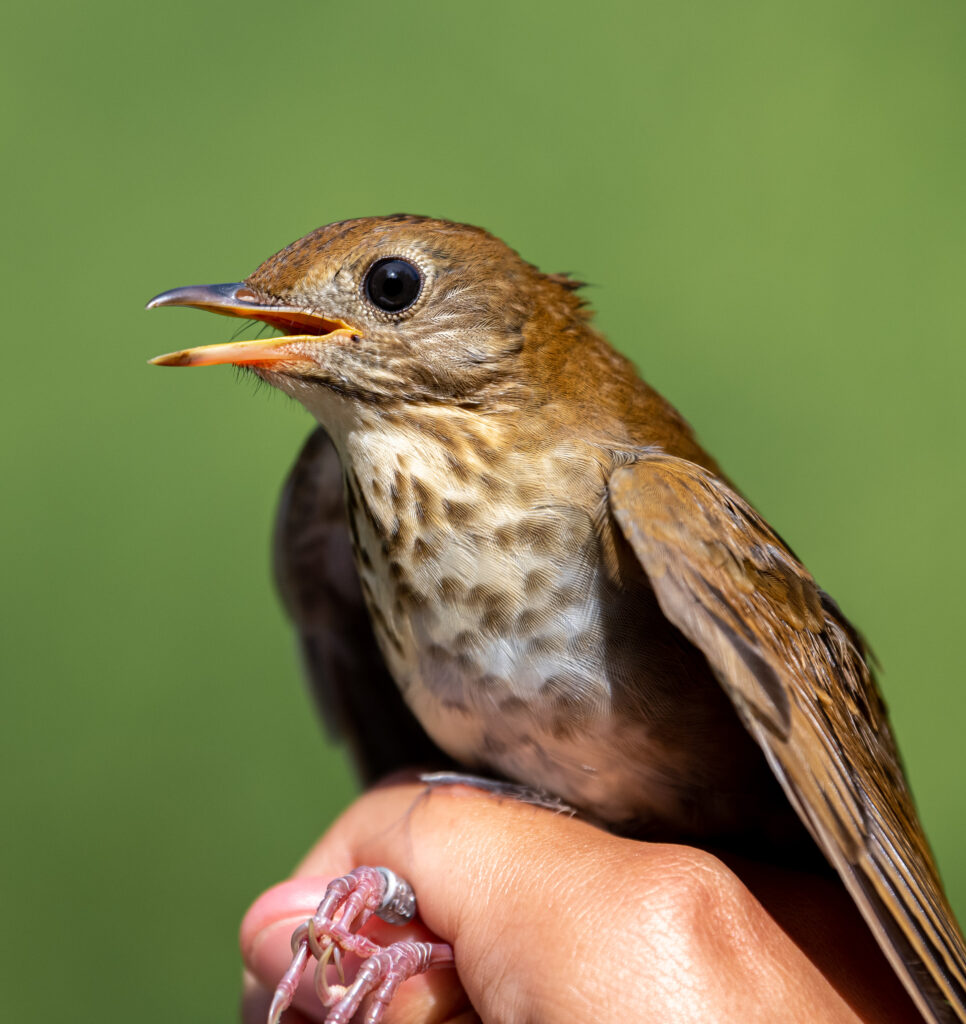
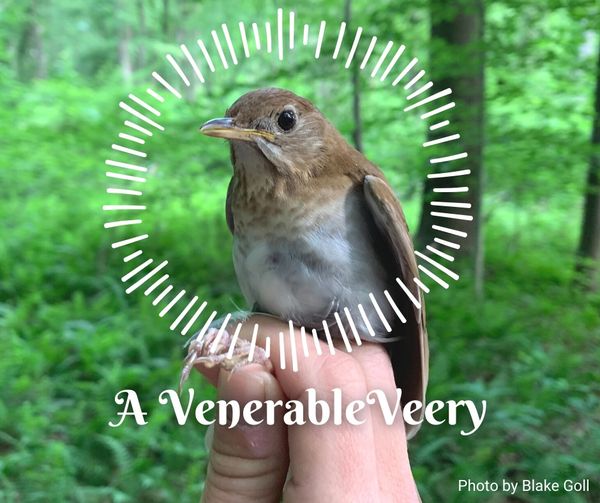
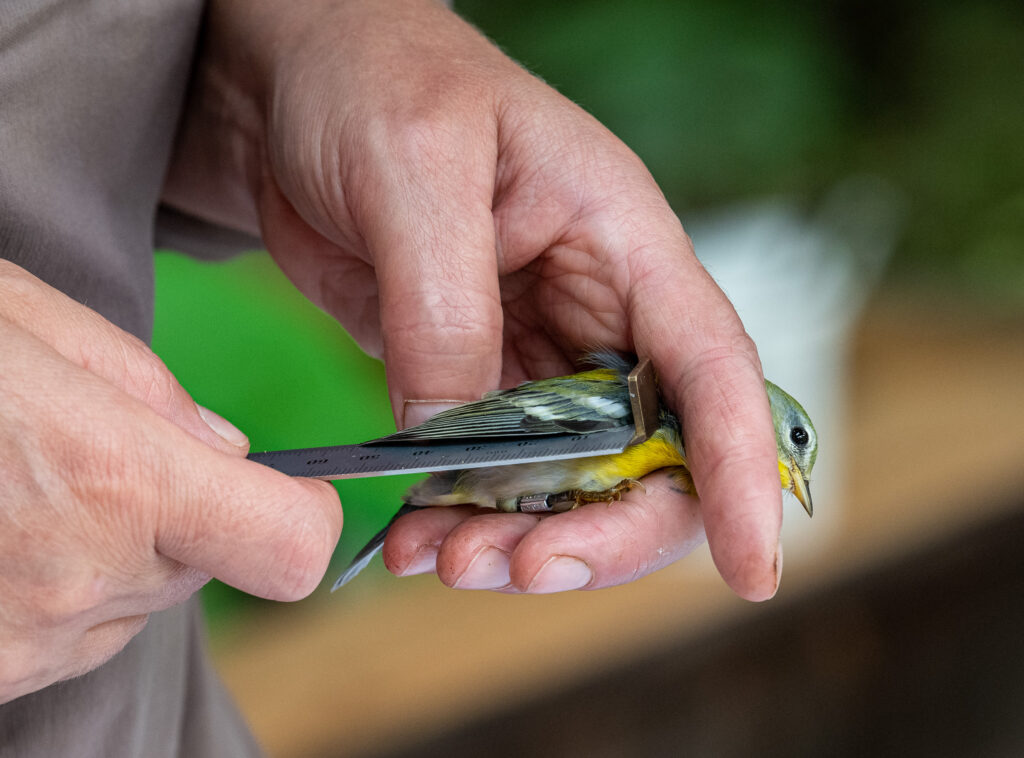
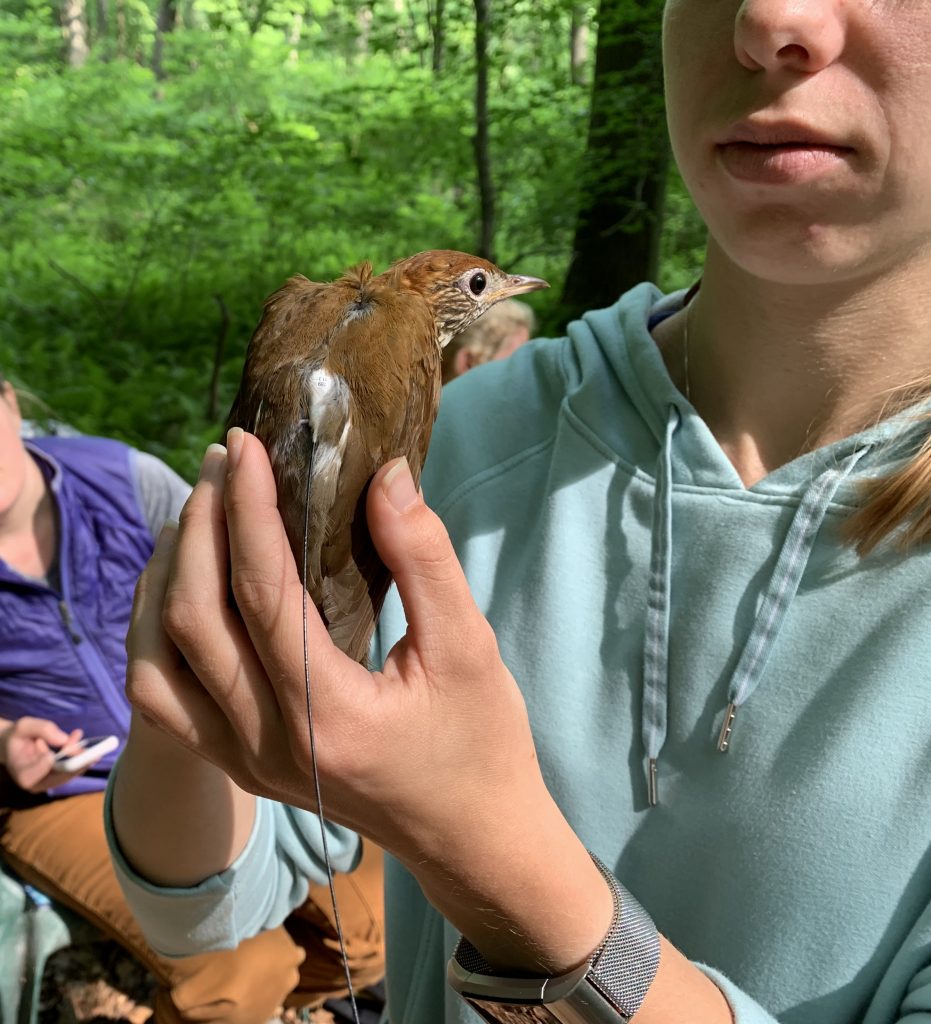
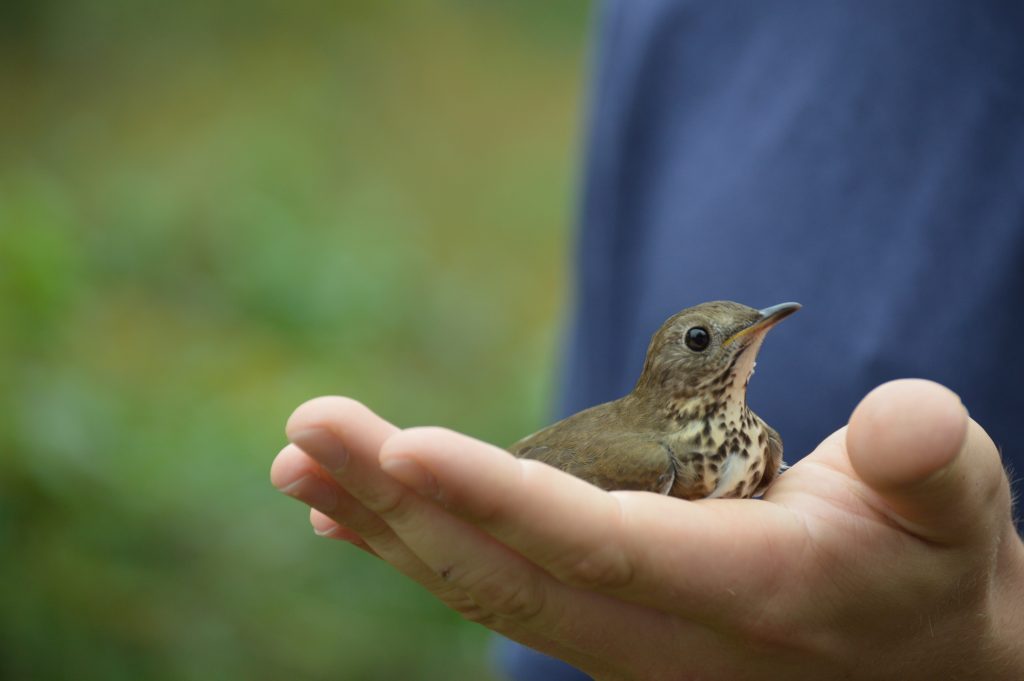
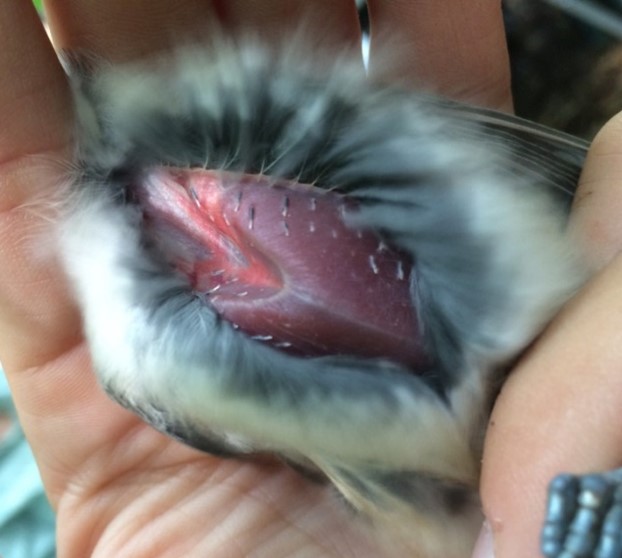
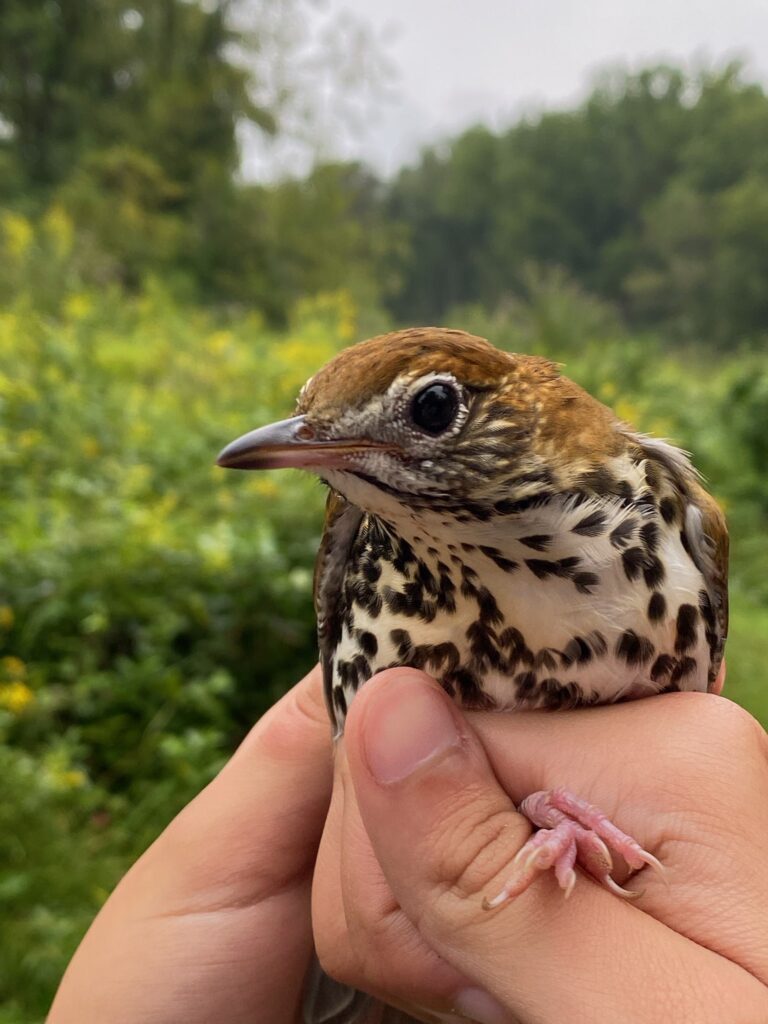
After the exhilaration of tracking spring migration in the hedgerows and thickets adjacent to the farm, the banders move to the interior woodlands of the preserve to monitor our breeding birds for the Institute for Bird Populations‘ constant-effort, nation-wide study called MAPS (Monitoring Avian Productivity and Survivorship). We sizzle beneath the cathedral-like canopy of the royal beeches and tulip poplars once every 10 days for 8 weeks in summer, using our mist nets to capture a snapshot of the nesting activity of Rushton Woods. Banding fresh, fuzzy babies just out of their nests is usually reward enough, but last summer we also had the humbling thrill of catching up with a “veery” old friend.
“It’s him!”, Alison exclaimed into the data book after I routinely read off the 9-digit band number of a recaptured Veery in hand. It was the same Veery we caught the year before and several years before that; it was the same Veery we first banded in 2011 (our inaugural MAPS year) when we proclaimed him to be at least 2 years old based on our feather and molt analysis. That makes him at least 12 years old as of summer of 2021 and our oldest banded bird for the station! (The oldest recorded Veery according to the Bird Banding Lab is 13.)
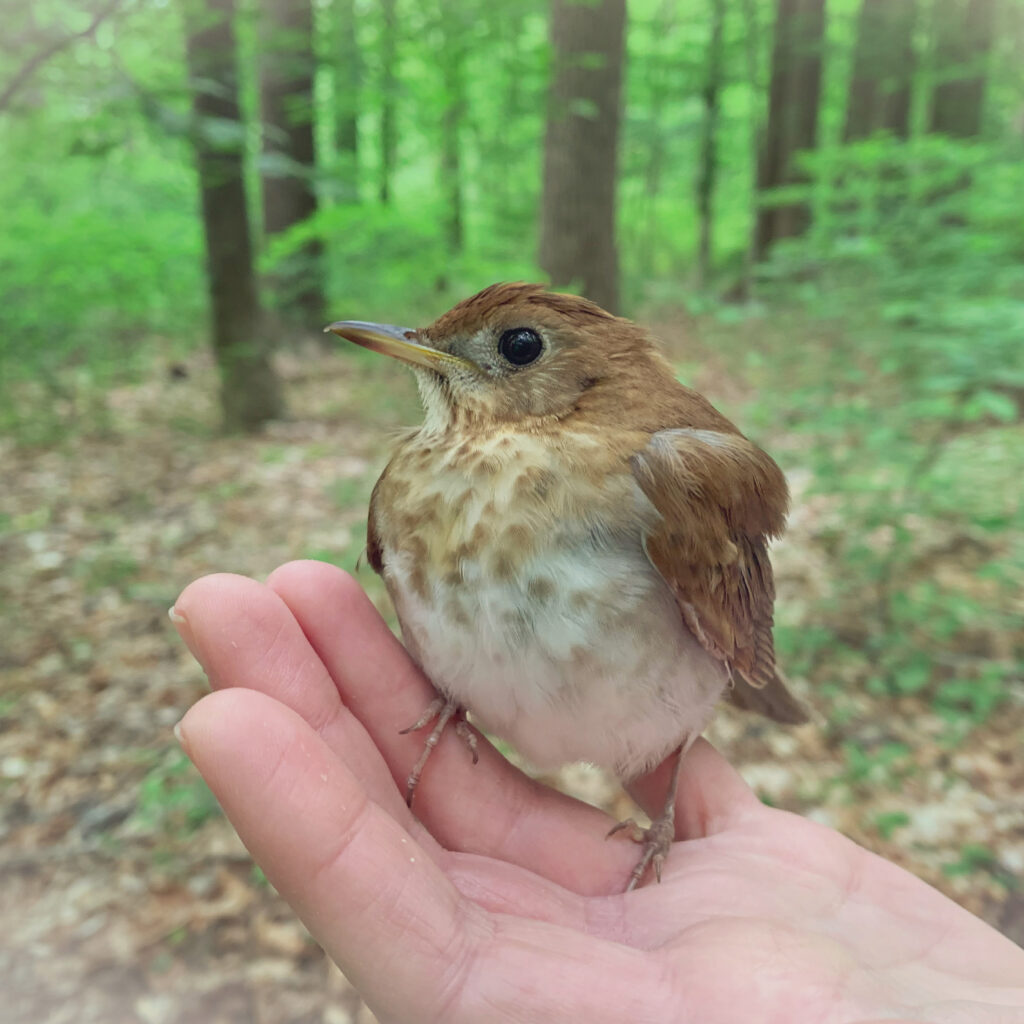

The Veery is a long-distance migrating, neotropical thrush—overwintering in central and southern Brazil—capable of flying 160 miles in one night. How awe-inspiring that our old Veery accomplished this feat a dozen times, triumphantly returning each summer to fill the emerald understory of Rushton with his ethereal song. An incredible longevity record such as this is a testament to the importance of preserving land for wild creatures. When you consider what these migratory birds must face on their journeys— habitat loss and destruction by humans, city lights and buildings, climate change, weather, pesticides, open oil pits, natural predators, and cats—it is miraculous that a bird can persist on such a knife’s edge.
Autumn’s Bounty
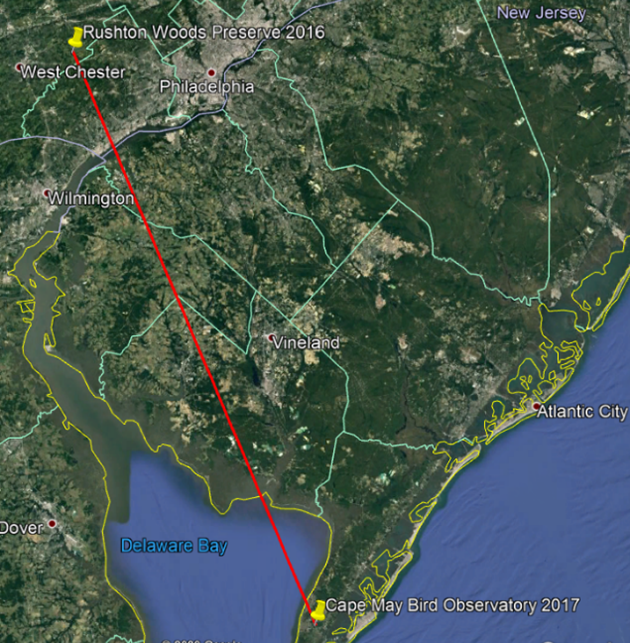
Fall brings Rushton banders back out to the migration station in the relatively open hedgerows; where young birds hatched in the dark woods find a more forgiving landscape for learning how to survive; and where migrants find an abundance of insect and berry forage to fuel their southbound journeys. Fall of 2021 turned out to be our second best with 1,372 new birds banded in addition to 174 recaptures of a total diversity of 61 species (fall of 2019 brought 1,427 new birds). Gray Catbirds—familiar and endearing garden birds related to mockingbirds— had a record year, comprising 42% of our total new birds! The majority of these were fresh youngsters hatched that summer; this annual recruitment of new birds into the population is the reason why we see a species-wide increase in abundance during the fall season relative to spring. (For comparison, Spring 2021 totaled 493 new birds.)
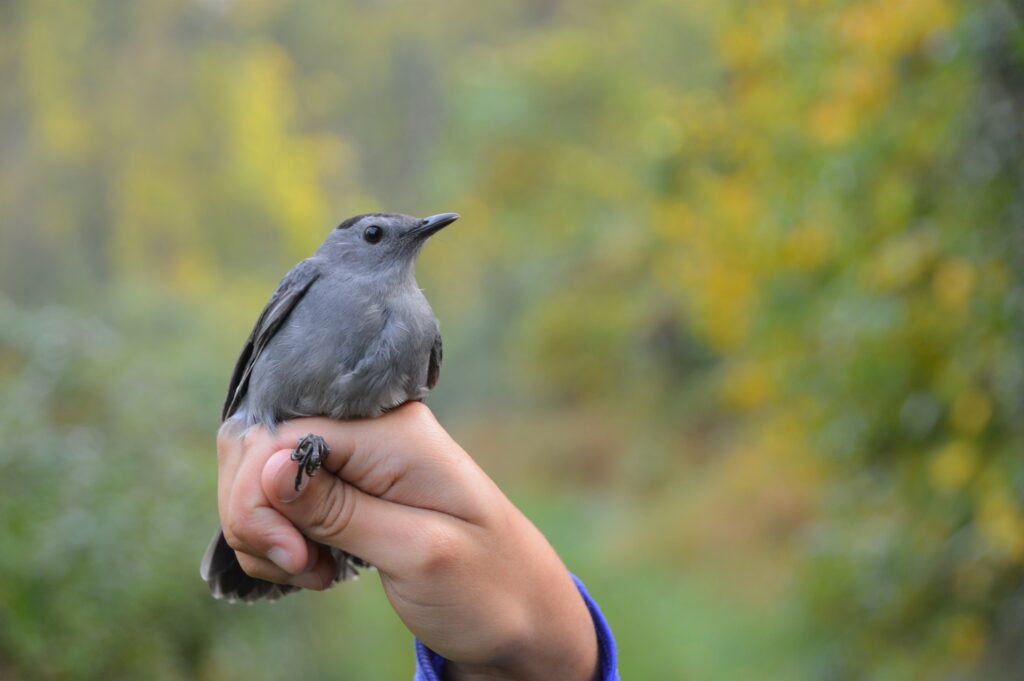

The fall banding season is also much longer than spring, with birds taking a more leisurely voyage in the absence of the pressure of mating. Last September brought beauties like the chartreuse Chestnut-sided Warbler, the dashing Black-throated Green Warbler, and the hard-for-every-birder-to-find Connecticut Warbler. (Our nets always manage to wrest a few skulking Connecticuts out of the dense scrub where they would otherwise go undetected.)
A young Yellow-billed Cuckoo, likely hatched that summer at Rushton, took center stage on September 14th. Having evolved one of the shortest nesting cycles of any bird—developing from hatching to fledging in a mind-blowingly short seven days (and snapping at flies from the nest at around Day 2)—allows for this species to capitalize on irruptively available food sources like noxious hairy caterpillars that other birds don’t dare to mess with.
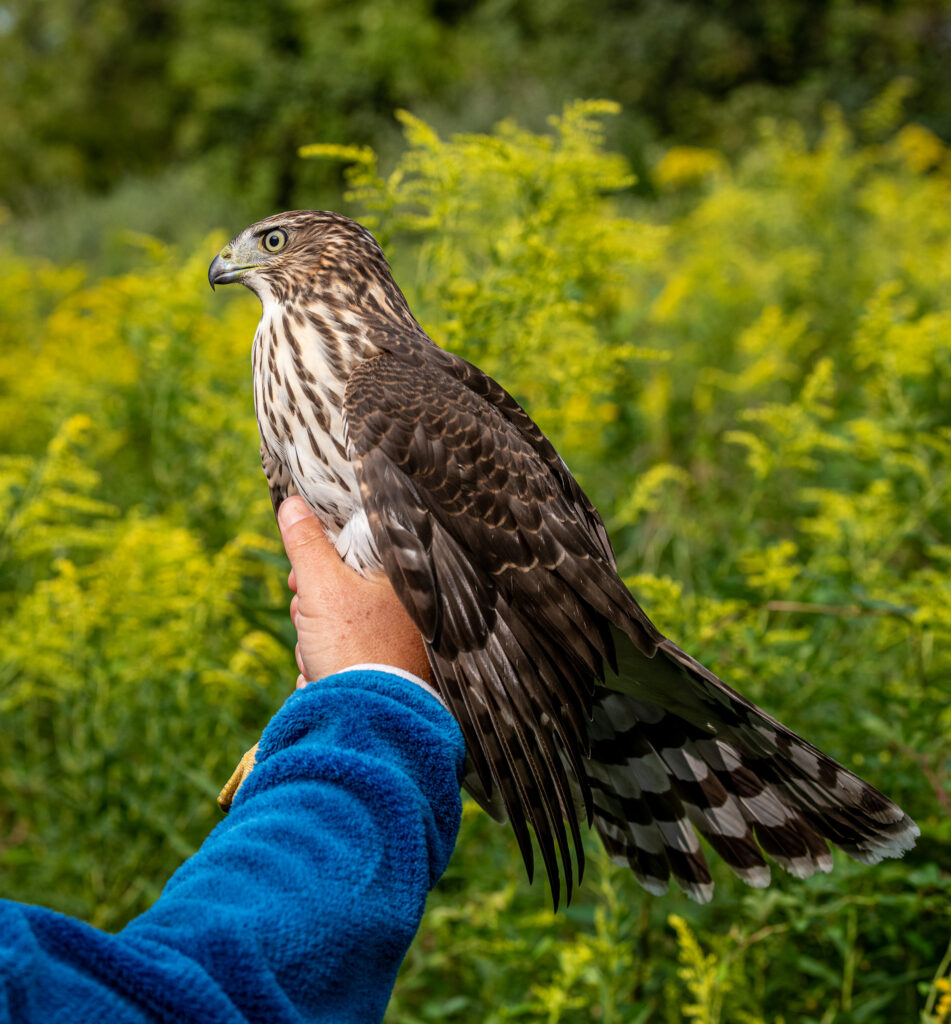
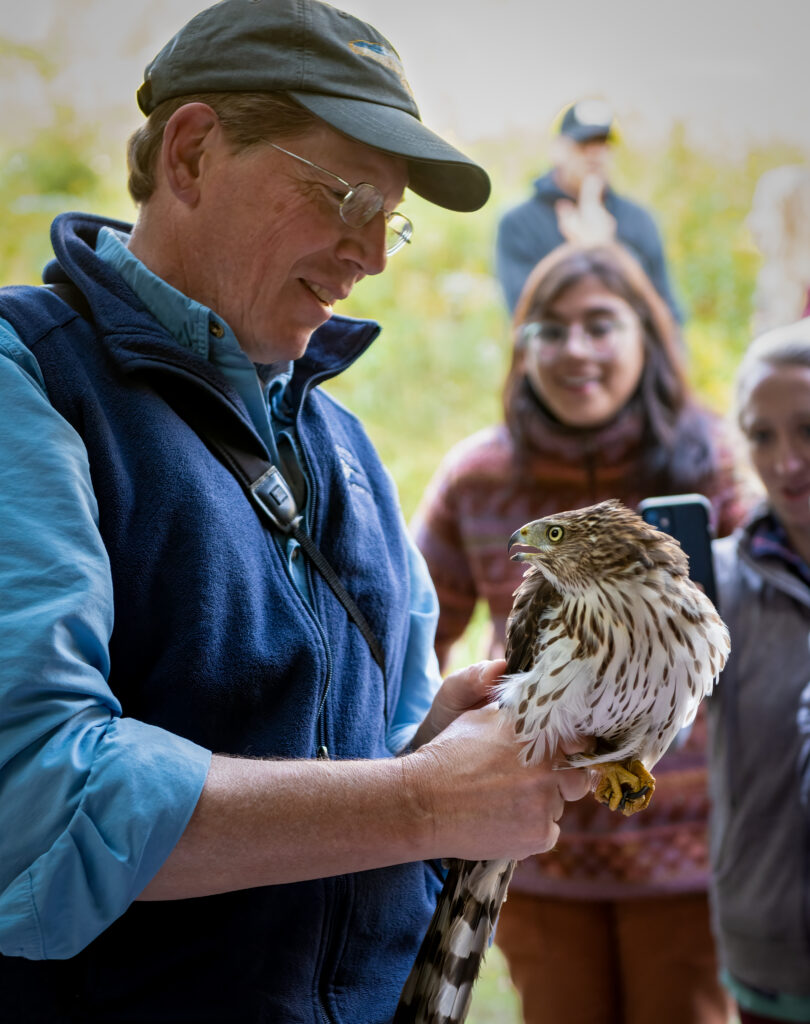
September 3oth produced our 102nd species for the station, a Cooper’s Hawk, that was ceremoniously banded by expert raptor bander and renowned naturalist and author, Scott Weidensaul. Scott happened to be visiting for a talk he was to give that evening about the Willistown Conservation Trust’s role in Motus Wildlife Tracking and his most recent book A World on the Wing: The Global Odyssey of Migratory Birds. After the raptorial hawk was gently banded and processed, it was temporarily excused from the net premises for the safety of the rest of our songbirds.
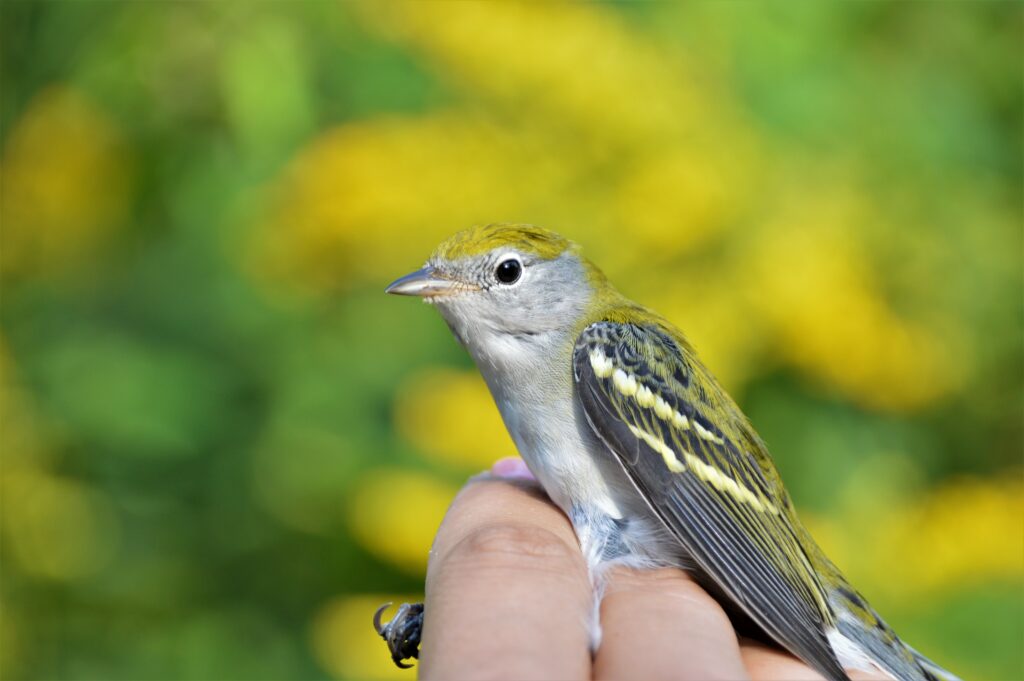
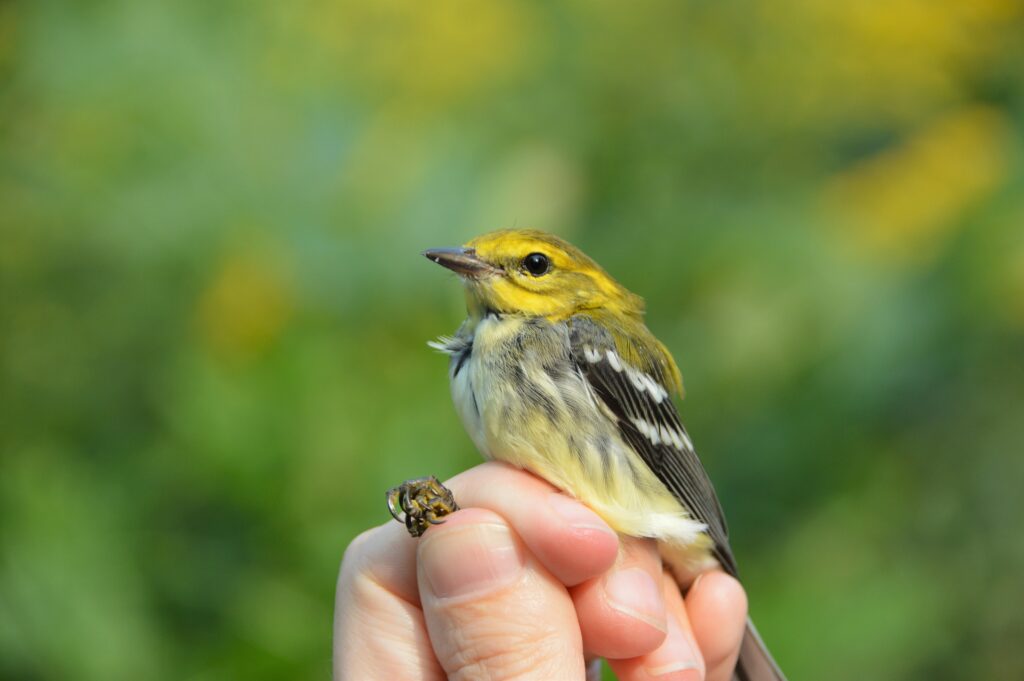
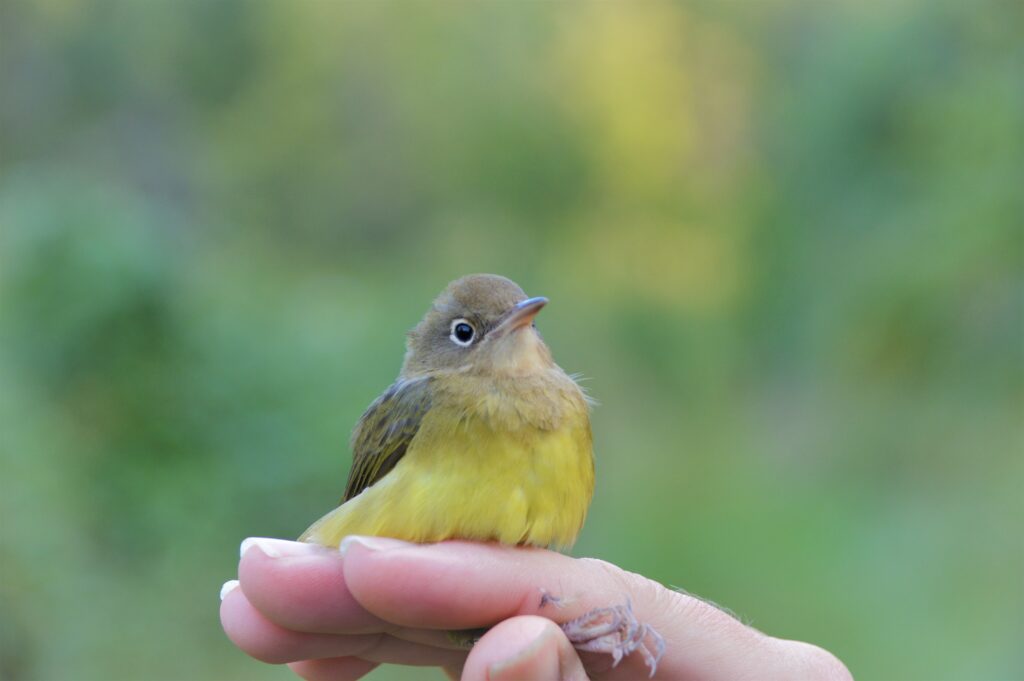
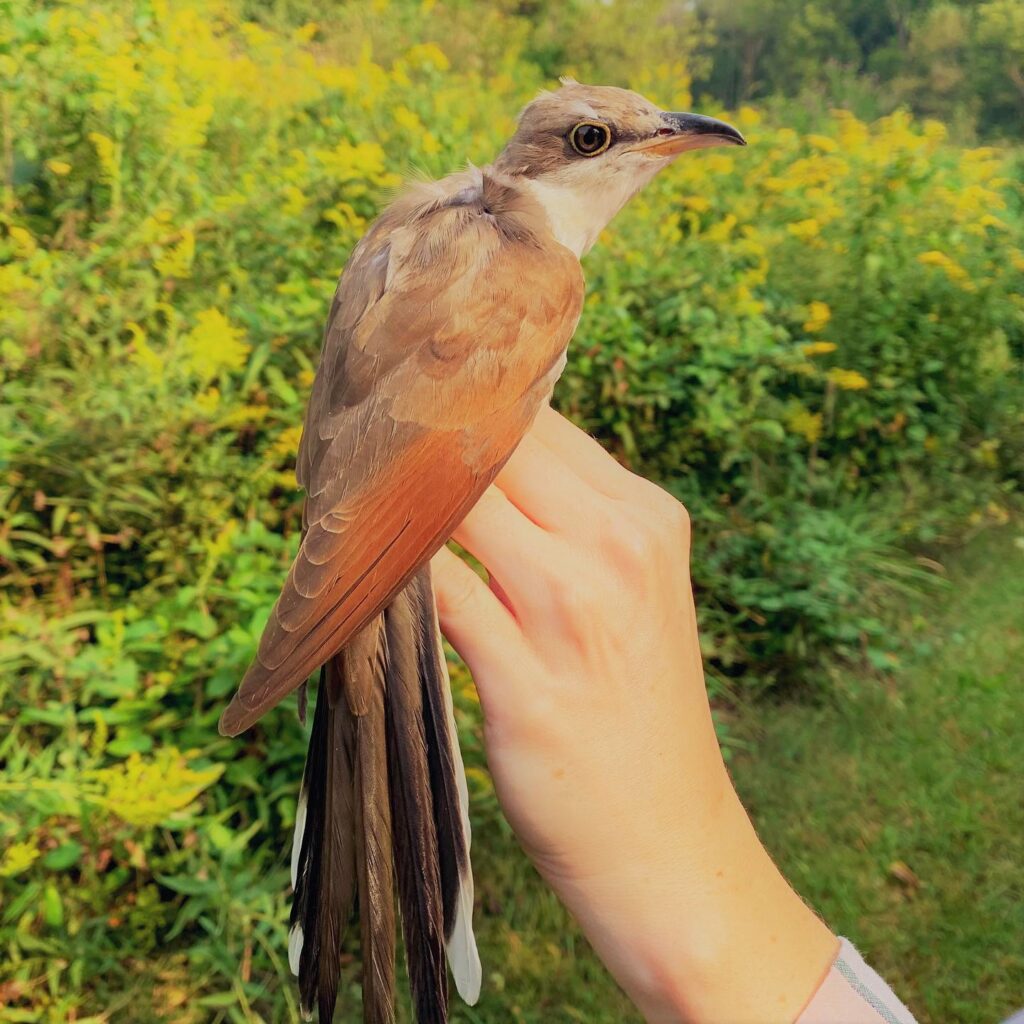





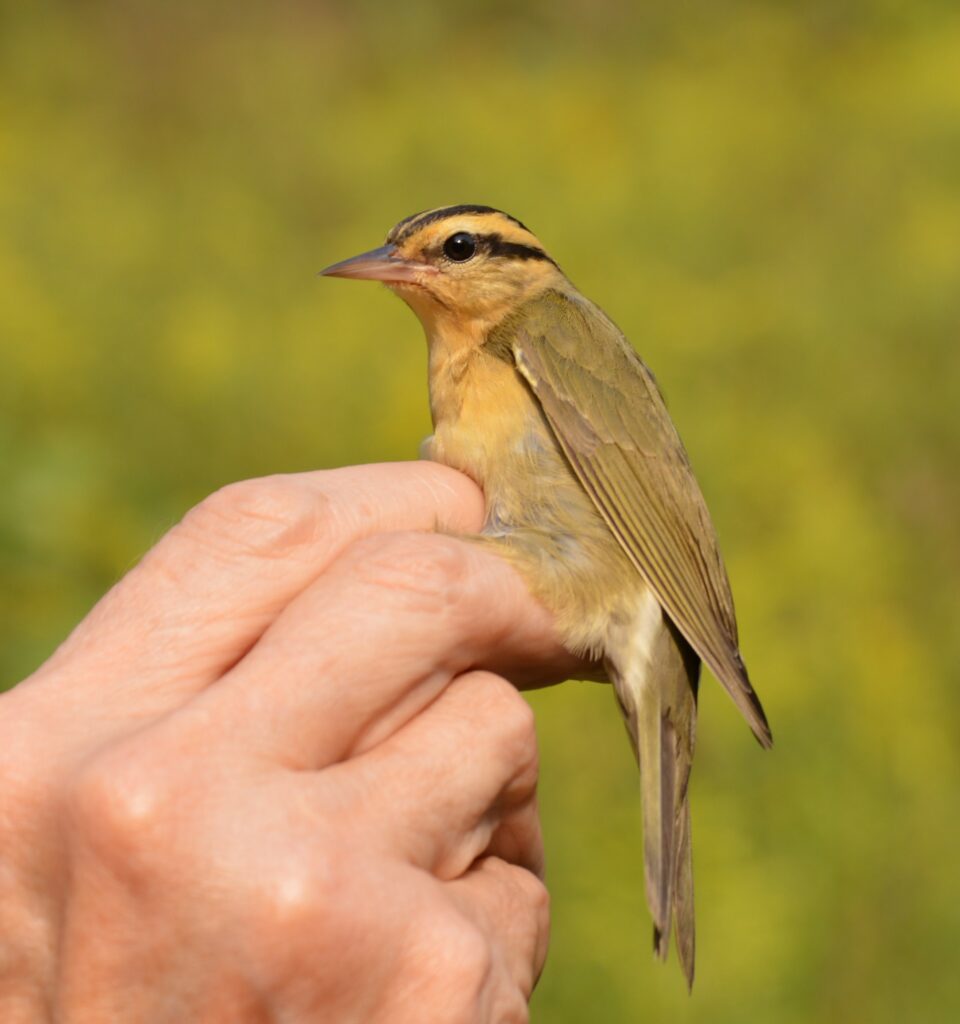
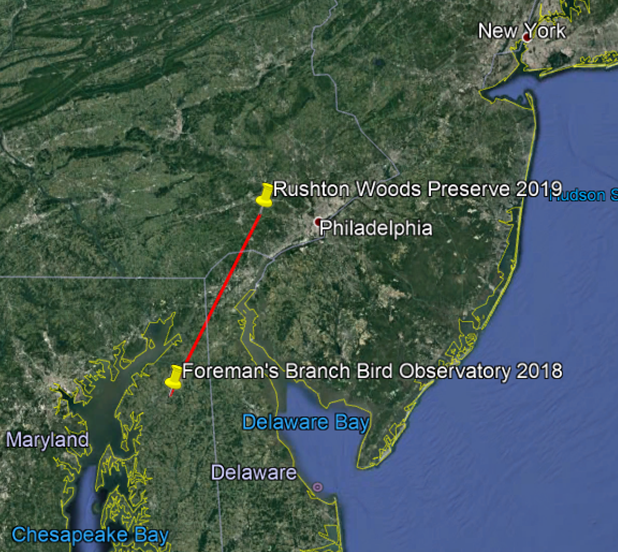
Also on that illustrious day of September 30th, we recaptured a young Worm-eating Warbler—originally banded by us on September 8th—that likely hatched that summer on a nearby wooded hillside. With a steady high fat score and consistent weight between catches, we assumed this brand new forest bird had dispersed from its natal grounds and was simply matriculating as a student in the bounty that Rushton’s shrublands have to offer. Recaptures like this illustrate the importance of shrub habitat for young birds (including those typically associated with forests) learning how to make a living before their first migration.
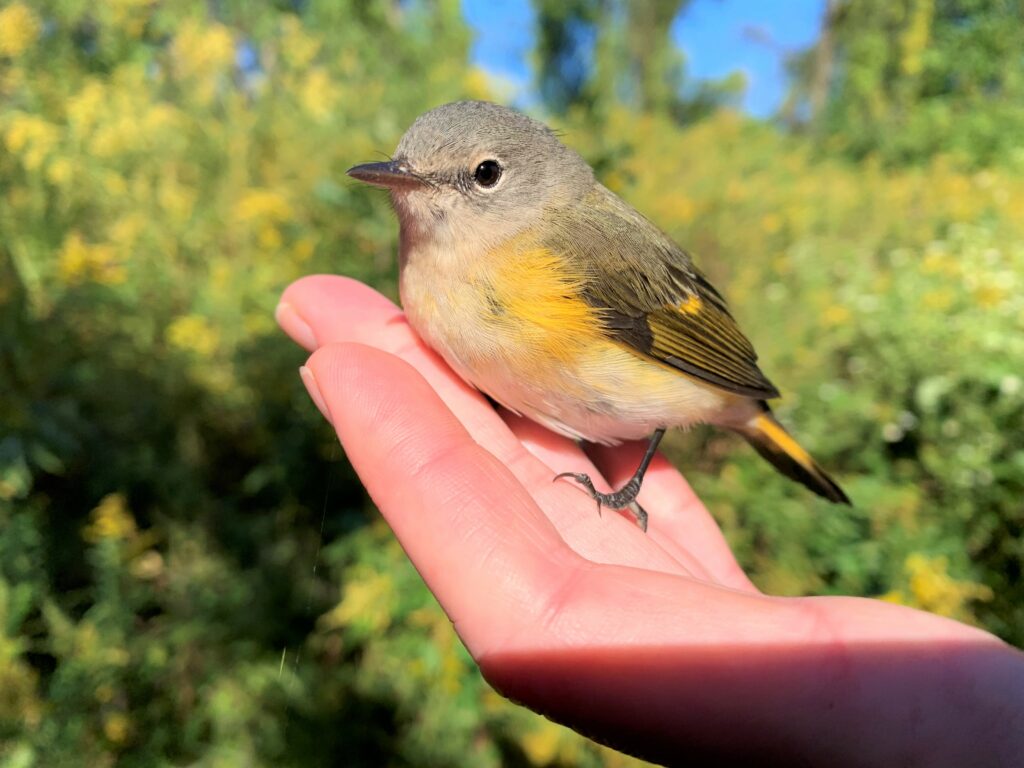
Other same-season recaptures illustrate the usage of the preserve as stopover habitat rather than “a school.” For example, last September we captured many American Redstarts—diminutive forest warblers that must refuel frequently during migratory journeys. One hatch year female that was caught multiple times gained 27% of her body weight in just 10 days; that’s the equivalent of a 145 pound human gaining almost 40 pounds in a little over a week! Birds gain weight in this rapid manner only to prepare for long overnight flights. Studying the rate of weight gain through recaptures such as these can help shed light on the quality of stopover habitat in terms of supplying adequate forage for migrants. (Lucky for us, a graduate student from University of Pennsylvania is analyzing our data for this as we speak.)


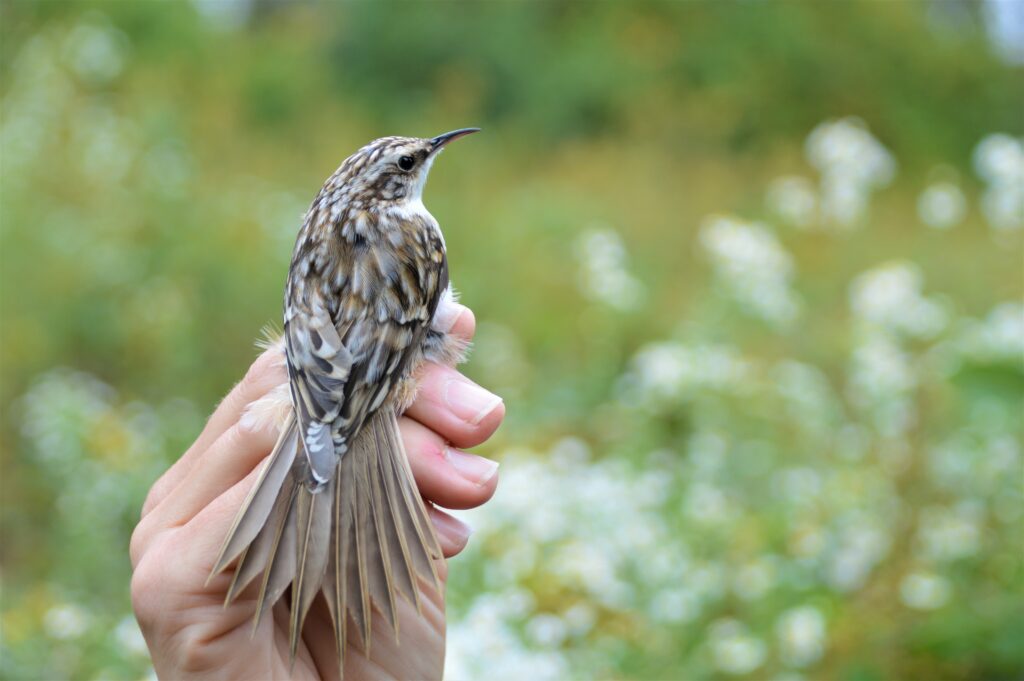
October brought muted treasures like the Brown Creeper—its bark colored plumage exquisitely flecked with the same snow white of the late blooming snakeroot; the Blackpoll Warbler with its racing tiger stripes and extraordinarily long wings that would carry it 1,800 miles nonstop over the Atlantic Ocean; and the Blue-headed Vireo with its distinguished alabaster spectacles and blue-gray hood for haunting evergreen hemlock forests.
Finally, one of the last days of the season produced our fourth ever American Woodcock! These marvelously camouflaged earthworm-eaters prefer early successional woodlots next to open fields (like those found at Rushton) where the males can perform their esoteric sky dances, electrifying the dusk and moonlit skies of spring with their wing twittering and chirping spiral descents.
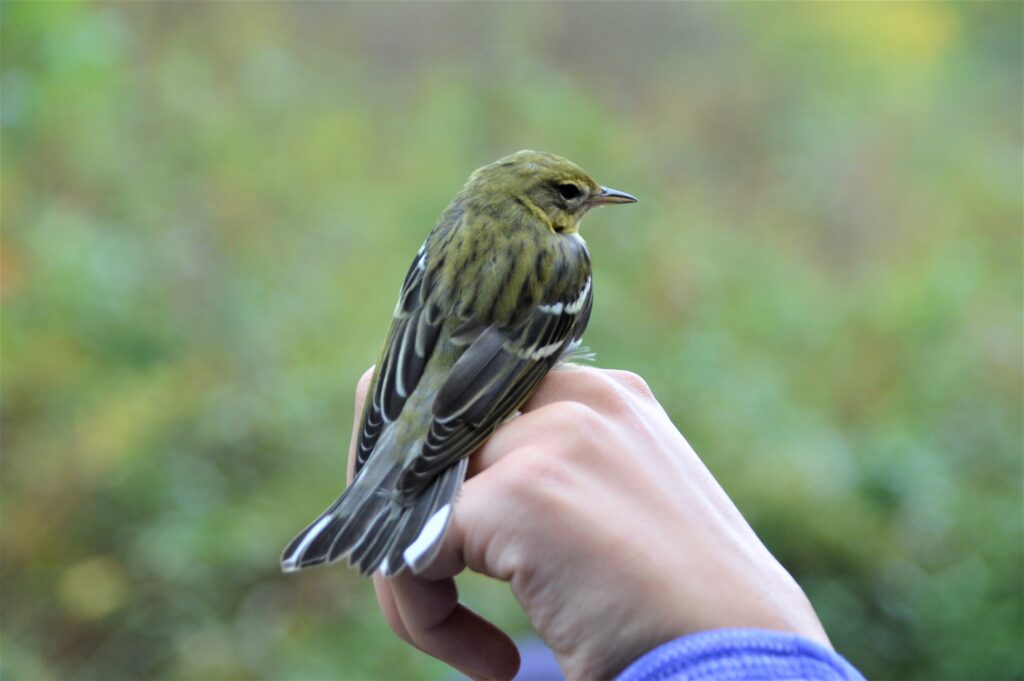
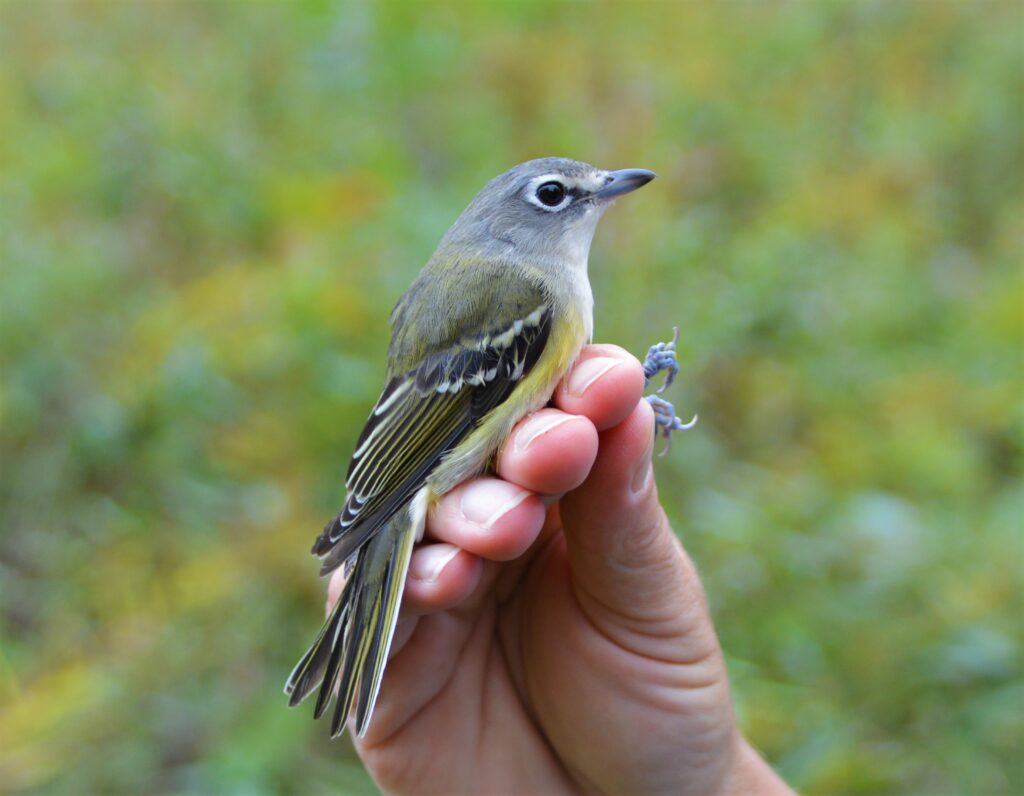
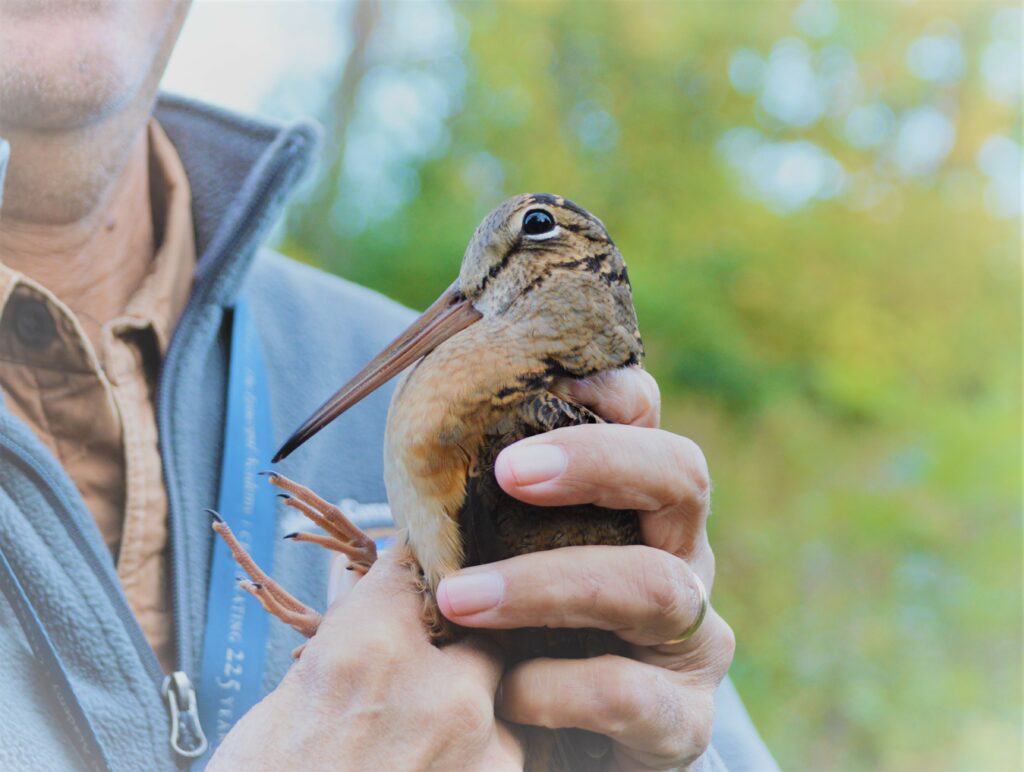




Bird Banding and Land Conservation
When all said and done, we banded nearly 2,000 birds in 2021 (between spring migration, summer MAPS, and fall migration). It was a wild year with fallouts, two new species for the station, discovering a bird that was with us since our very first year, hosting and educating hundreds of visitors including special guests, and training many students and colleagues. Through banding we continue to learn information about species abundance and diversity, individual longevity and site fidelity, and how birds are using our conserved land throughout their annual cycle.
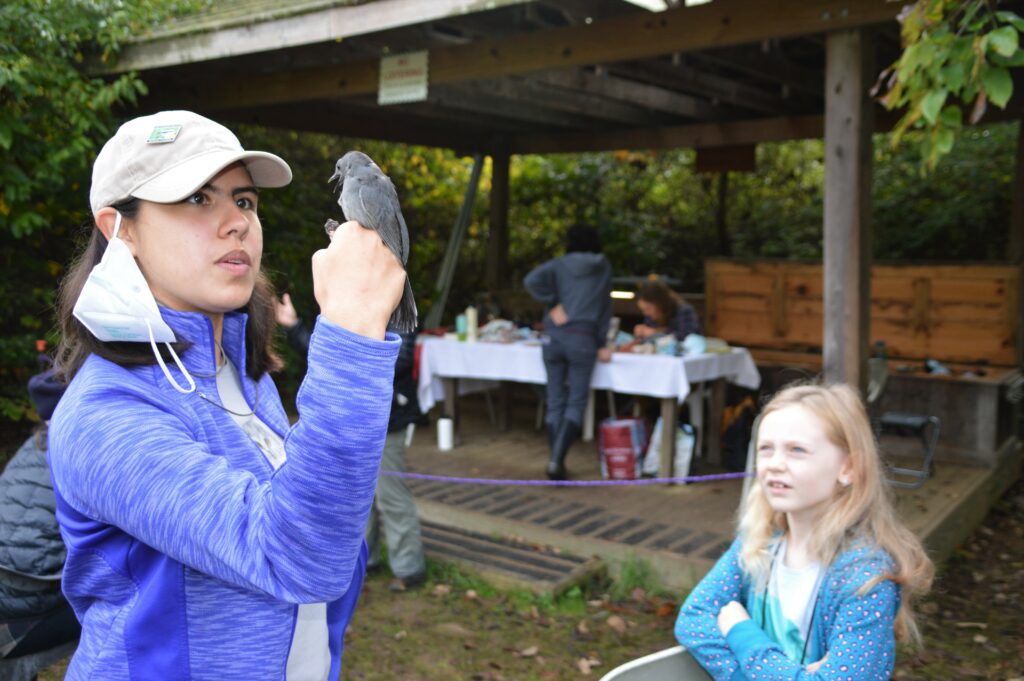
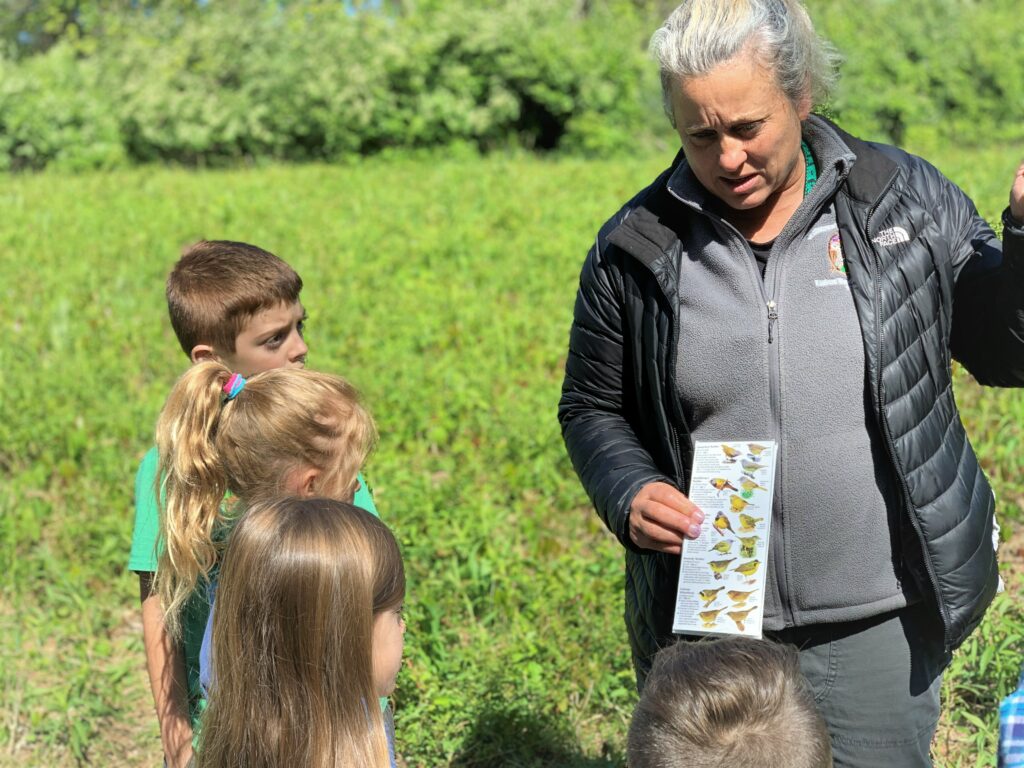
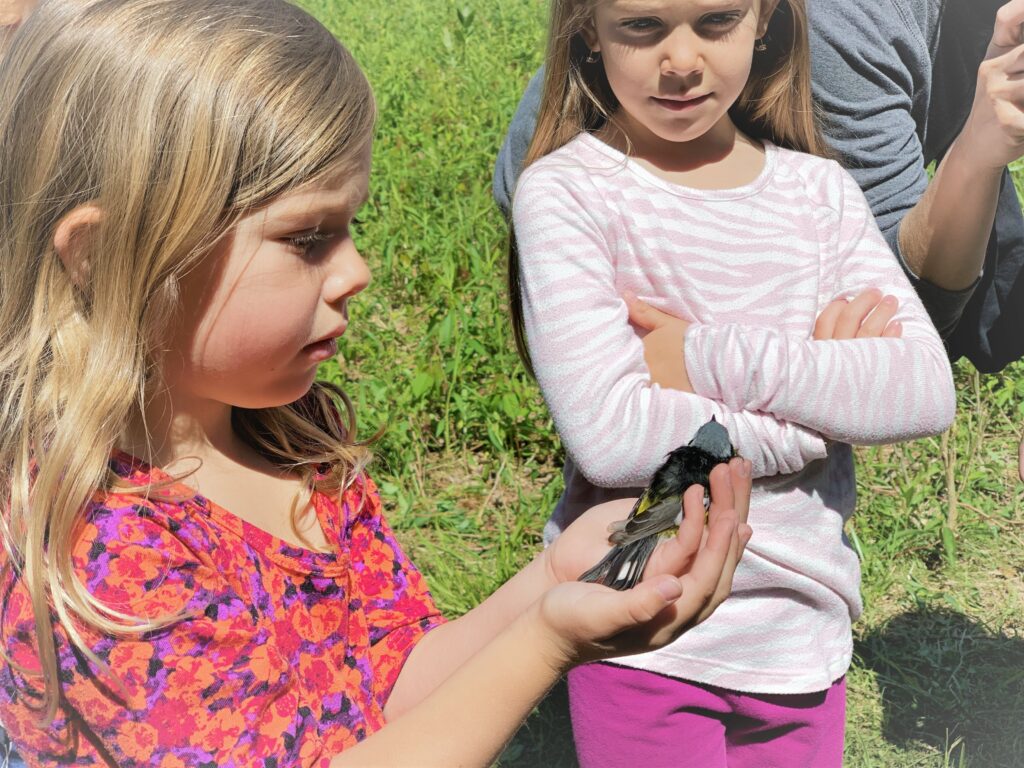
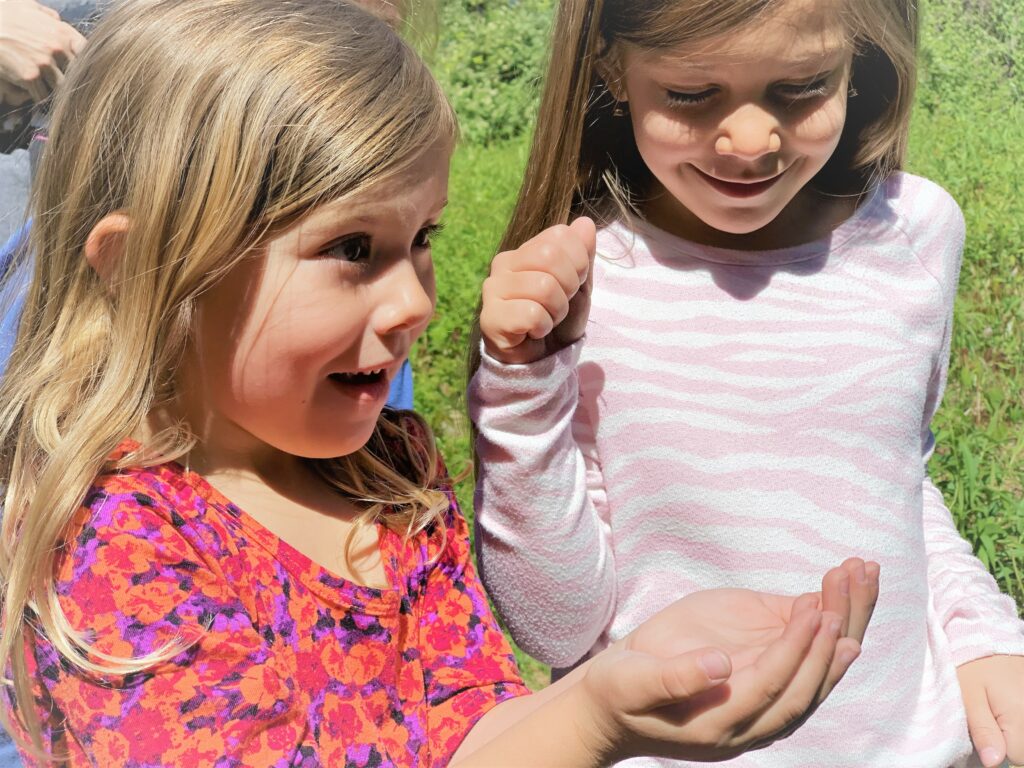





Our banding station’s high catch rates (or “birdiness”) combined with the unique setting on a regenerative farm within a greater nature preserve shows the world that people and wildlife can coexist in harmony. On a broader scale as Rushton Woods becomes surrounded by increasing human development, our continuous banding efforts may be illuminating the preserve as a critical island habitat for birds traveling through, wintering, or breeding in the region.
The gravity of the state of birds today runs the risk of being lost on the reader through an auspicious annual banding report such as this. It must be noted that in less than one human lifetime, North American bird populations have plummeted by 30% with no ecosystem spared; that’s 3 billion, or one in four birds gone since 1970, largely due to human actions. So while we recover from our world being briefly disrupted by the uncertainty of a pandemic, we must learn to minimize our disruption of the natural systems to which we are inextricably linked. (Visit #BringBirdsBack)
One thing’s for certain: wild will always be welcome at Rushton, where the rhythm of winged creatures reigns.